Protease-Activated Receptor-2, amide
CAS No. 190383-13-2
Protease-Activated Receptor-2, amide( —— )
Catalog No. M30034 CAS No. 190383-13-2
Protease-Activated Receptor-2, amide (SLIGKV-NH2) is a highly potent protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) activating peptide.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 63 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 106 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 181 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 272 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 408 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameProtease-Activated Receptor-2, amide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionProtease-Activated Receptor-2, amide (SLIGKV-NH2) is a highly potent protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) activating peptide.
-
DescriptionProtease-Activated Receptor-2, amide (SLIGKV-NH2) is a highly potent protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) activating peptide.(In Vitro):The PAR2-activating peptides used are: SLIGKV-OH, SLIGRL-OH, SLIGKV-NH2, SLIGRL-NH2. The synthetic agonist peptides mimicking the tethered ligand of PAR2, Ser-Leu-Ile-Gly-Lys-Val (SLIGKV-OH), Ser-Leu-Ile-Gly-Arg-Leu (SLIGRL-OH) and their amidated forms Ser-Leu-Ile-Gly-Lys-Val-amide (SLIGKV-NH2) Ser-Leu-Ile-Gly-Arg-Leu-amide (SLIGRL-NH2) have also been demonstrated being able to activate the receptor without enzymatic cleavage, therefore, have been utilised as biological tools to examine physiological functions of PAR2. Protease-Activated Receptor-2, amide is one of a four family subgroup of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), called PARs. Protease-activated receptors are distinguished from other GPCRs through their unique proteolytic mechanism of activation. For PAR2, activating proteases, such as trypsin, tryptase and coagulation factors VIIa and Xa, cleave a specific extracellular amino-terminal domain of the receptor to reveal a "tethered ligand", SLIGKV- and SLIGRL- for human and mouse/rat PAR2, respectively, which subsequently interacts with the activation domain of the receptor, initiating intracellular signaling pathways. The protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, and is expressed in a wide variety of human tissues and cells. PAR2 belongs to a family of seven transmembrane domain receptor proteins that are activated by proteolysis. Enzymatic digestion exposes an N-terminus ligand sequence that binds intramolecularly to the activation site on the extracellular loop II, initiating a G-protein-mediated cell-signalling cascade and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)-regulated gene transcription.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetPAR
-
RecptorPAR2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number190383-13-2
-
Formula Weight614.78
-
Molecular FormulaC28H54N8O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O : 33.33 mg/mL (54.21 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILES——
-
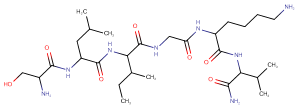
Chemical NameSequence:Ser-Leu-Ile-Gly-Lys-Val-NH2
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Kanke T, et al. Binding of a highly potent protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) activating peptide, [3H]2-furoyl-LIGRL-NH2, to human PAR2. Br J Pharmacol. 2005 May;145(2):255-63.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Protease-Activated R...
Protease-Activated Receptor-4 is the proteinase-activated receptor-4 (PAR4) ?agonist.
-
I-191
I-191 is a potent antagonist of protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2)?inhibits multiple signaling functions in human cancer cells.?
-
Parstatin (human)
Cell-permeable peptide cleaved from protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) upon receptor activation. Attenuates endothelial cell migration and proliferation (IC50 ~ 3 μM), and induces cell cycle arrest. Promotes activation of caspase-3 and exhibits pro-apoptotic activity in vitro. Inhibits angiogenesis and exhibits cardioprotective activity in vivo.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


