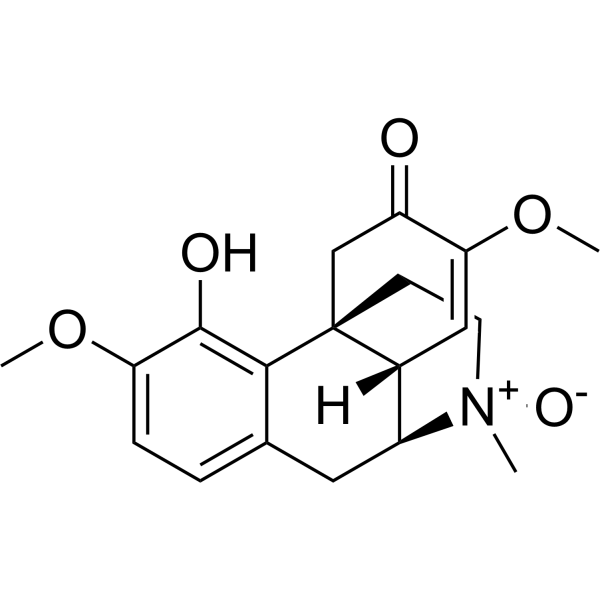
Sinomenine N-oxide
CAS No. 1000026-77-6
Sinomenine N-oxide( —— )
Catalog No. M29455 CAS No. 1000026-77-6
Sinomenine N-oxide is one of the major metabolites of the cyclic metabolic mechanism of Sinomenine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 377 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 188 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 277 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSinomenine N-oxide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSinomenine N-oxide is one of the major metabolites of the cyclic metabolic mechanism of Sinomenine.
-
DescriptionSinomenine N-oxide is one of the major metabolites of the cyclic metabolic mechanism of Sinomenine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1000026-77-6
-
Formula Weight345.39
-
Molecular FormulaC19H23NO5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[H][C@]1([C@@]2(C3)C4=C(O)C(OC)=CC=C4C[C@]1([H])[N+](C)([O-])CC2)C=C(OC)C3=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
PU.1-IN-1
PU.1-IN-1 is a potent PU.1 inhibitor (IC50 : 2 nM) with anti-inflammatory activity.
-
Octadecyl Rhodamine ...
Octadecyl Rhodamine B chloride, also known as RBOE, is a polarity-sensitive dye that is often used as a chromophore with other compounds to stain cell membranes and has applications in the assembly of organic molecules, in membrane structures and in the transfer of electron energy in the structural domains of proteins.
-
H-Arg(Pbf)-OMe hydro...
H-Arg(Pbf)-OMe hydrochloride is an arginine analogue.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


