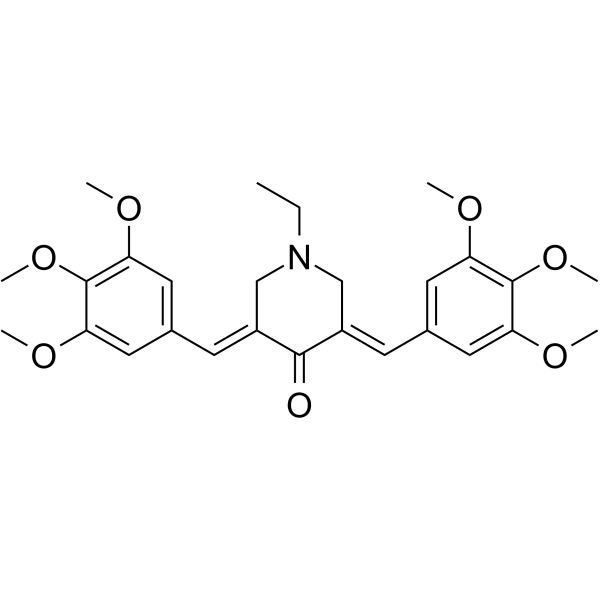
L48H37
CAS No. 343307-76-6
L48H37( —— )
Catalog No. M28299 CAS No. 343307-76-6
L48H37 is an analog of Curcumin (HY-N0005) with improved chemical stability. L48H37 is a potent and specific myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD2) inhibitor and inhibits the interaction and signaling transduction of LPS-TLR4/MD2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 92 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 187 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 291 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 477 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 671 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL48H37
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL48H37 is an analog of Curcumin (HY-N0005) with improved chemical stability. L48H37 is a potent and specific myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD2) inhibitor and inhibits the interaction and signaling transduction of LPS-TLR4/MD2.
-
DescriptionL48H37 is an analog of Curcumin (HY-N0005) with improved chemical stability. L48H37 is a potent and specific myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD2) inhibitor and inhibits the interaction and signaling transduction of LPS-TLR4/MD2. (In Vitro):L48H37 inhibits LPS-induced inflammation, particularly TNF-α and IL-6 production and gene expression in mouse macrophages .L48H37 (0-20 μM; 24 hours) decreases the viability of A549 and H460 cells with IC 50 values of 5.3 μM and 2.3 μM, respectively, which is more effective compared to curcumin in lung cancer cells. It shows a low cytotoxicity on normal human lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) with IC 50 of 21 μM .L48H37 (1, 2, or 4 μM; 16 hours) dose‐dependently inhibited the expression of p‐Cdc2 and Cdc2, and increases the expression of p53. It also shows increased levels of cleaved poly (ADP‐ribosyl) polymerase (PARP) and reduced levels of anti‐apoptotic protein Bcl‐2 in H460 and A549 cells .L48H37 (4 μM; 16 hours) rapidly induces intracellular ROS levels dose-dependently as detected by increased DCF levels in H460 and A549 cells . Cell Viability Assay Cell Line: A549 and H460 cells; BEAS-2B cells Concentration: 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 20μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Inhibited lung cancer cells growth in a concentration-dependent manner. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line: A549 and H460 cells Concentration: 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 20μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Decreased p‐Cdc2, Cdc2, and Bcl‐2 expression in 2 lung cancer cells.(In Vivo):L48H37 (intraperitoneal injection; 5 mg or 10 mg/kg; once daily; 11‐day) inhibits H460 xenograft tumor growth and exhibits anti‐tumor activity in mice . Animal Model: 5‐week‐old athymic BALB/cA nu/nu female mice (18‐22 g) Dosage: 5 mg or 10 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; once daily; 11‐day Result: Reduced tumor wet weights as compared to vehicle control.Decreased the levels of p‐STAT3, and increased the levels of p‐EIF2α and ATF4 in vivo.Exhibited no significant structural changes in mice.
-
In VitroL48H37 inhibits LPS-induced inflammation, particularly TNF-α and IL-6 production and gene expression in mouse macrophages.L48H37 (0-20?μM; 24 hours) decreases the viability of A549 and H460 cells with IC50 values of 5.3?μM and 2.3?μM, respectively, which is more effective compared to curcumin in lung cancer cells. It shows a low cytotoxicity on normal human lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) with IC50?of 21?μM.L48H37 (1, 2, or 4?μM; 16 hours) dose‐dependently inhibited the expression of p‐Cdc2 and Cdc2, and increases the expression of p53. It also shows increased levels of cleaved poly (ADP‐ribosyl) polymerase (PARP) and reduced levels of anti‐apoptotic protein Bcl‐2 in H460 and A549 cells.L48H37 (4?μM; 16?hours) rapidly induces intracellular ROS levels dose-dependently as detected by increased DCF levels in H460 and A549 cells. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:A549 and H460 cells; BEAS-2B cells Concentration:0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 20?μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Inhibited lung cancer cells growth in a concentration-dependent manner. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:A549 and H460 cells Concentration:0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 20?μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Decreased p‐Cdc2, Cdc2, and Bcl‐2 expression in 2 lung cancer cells.
-
In VivoL48H37 (intraperitoneal injection; 5?mg or 10?mg/kg; once daily; 11‐day?) inhibits H460 xenograft tumor growth and exhibits anti‐tumor activity in mice. Animal Model:5‐week‐old athymic BALB/cA nu/nu female mice (18‐22?g) Dosage: 5?mg or 10?mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; once daily; 11‐day Result:Reduced tumor wet weights as compared to vehicle control.Decreased the levels of p‐STAT3, and increased the levels of p‐EIF2α and ATF4 in vivo.Exhibited no significant structural changes in mice.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorNO Synthase|TNF-α|NOS|inflammation|CCL4|Antioxidant
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number343307-76-6
-
Formula Weight483.55
-
Molecular FormulaC27H33NO7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (103.40 mM)
-
SMILESCCN1CC(=CC2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C(OC)=C2)C(=O)C(C1)=CC1=CC(OC)=C(OC)C(OC)=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lin CH, et al. Eburicoic Acid, a Triterpenoid Compound from Antrodia camphorata, Displays Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects in Palmitate-Treated C2C12 Myotubes and in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.?Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2314. Published 2017 Nov 2.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dicurone
Glucuronolactone is a naturally occurring chemical that is an important structural component of nearly all connective tissues. Glucuronolactone is also found in many plant gums.
-
PKA Inhibitor Substr...
PKA Inhibitor Substrate
-
β-Glycerophosphate d...
β-Glycerophosphate is a classical serine-threonine phosphatase inhibitor used in kinase reaction buffers. BGP is often used in combination with other phosphatase/protease inhibitors for broad spectrum inhibition.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


