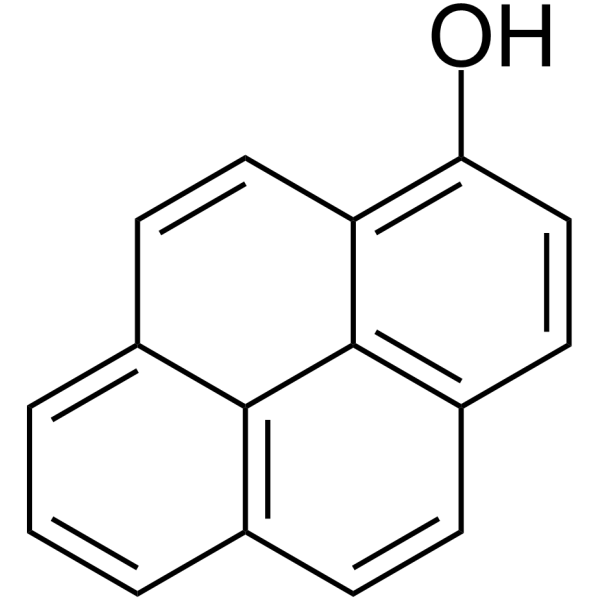
1-Hydroxypyrene
CAS No. 5315-79-7
1-Hydroxypyrene( Pyren-1-ol | 1-Pyrenol )
Catalog No. M27047 CAS No. 5315-79-7
1-Hydroxypyrene, a biomarker of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, is analyzed in urine samples.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1-Hydroxypyrene
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-Hydroxypyrene, a biomarker of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, is analyzed in urine samples.
-
Description1-Hydroxypyrene, a biomarker of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, is analyzed in urine samples.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsPyren-1-ol | 1-Pyrenol
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorERβ
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5315-79-7
-
Formula Weight218.255
-
Molecular FormulaC16H10O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (229.08 mM)
-
SMILESOc1ccc2ccc3cccc4ccc1c2c34
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Gregory Lee Durst, et al. Substituted benzopyrans as selective estrogen receptor-beta agonists. EP1626974B1
molnova catalog



related products
-
7-Ketolithocholic ac...
7-Ketolithocholic acid (3α-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5β-cholanic acid) can be absorbed and suppresses endogenous bile acid production and biliary cholesterol secretion.
-
(S)-3-Hydroxybutanoi...
(S)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid is a normal human metabolite that has been found elevated in geriatric patients remitting from depression.
-
Spermidine
Spermidine inhibits NOS1 (nNOS). Spermidine binds and precipitates DNA and may be used for purification of DNA binding proteins. Spermidine activates PNK (polynucleotide kinase T4). Spermidine binds to and activates NMDA and has been shown to potentiate NMDA-induced currents in a concentration-dependent manner.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


