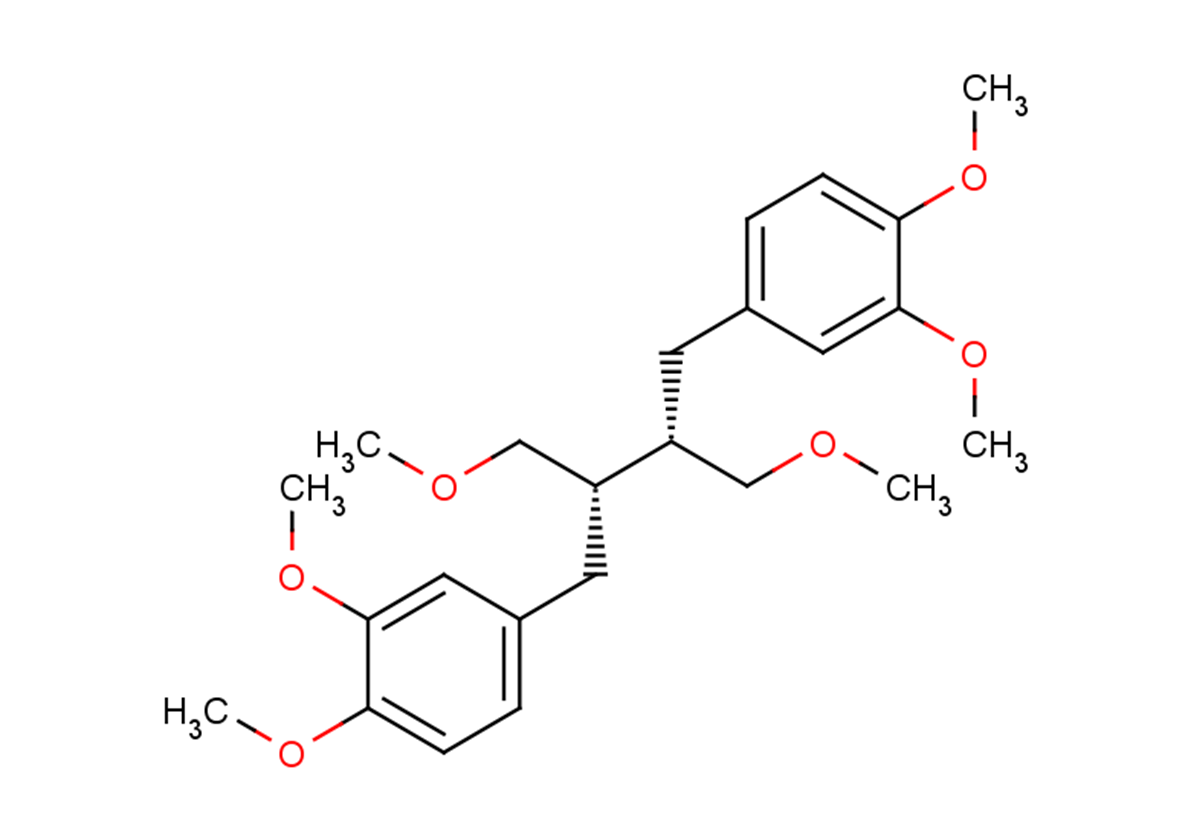
Phyllanthin
CAS No. 10351-88-9
Phyllanthin( —— )
Catalog No. M23242 CAS No. 10351-88-9
Phyllanthin is widely used as hepatoprotective and antigenotoxic and inhibit function of P-gp.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 136 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 117 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 282 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePhyllanthin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPhyllanthin is widely used as hepatoprotective and antigenotoxic and inhibit function of P-gp.
-
DescriptionPhyllanthin is widely used as hepatoprotective and antigenotoxic and inhibit function of P-gp.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetNF-κB
-
RecptorNF-κB
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number10351-88-9
-
Formula Weight418.5
-
Molecular FormulaC24H34O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 62.5 mg/mL (149.34 mM)
-
SMILESCOC[C@@H](CC1=CC=C(OC)C(OC)=C1)[C@@H](COC)CC2=CC=C(OC)C(OC)=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Phyllanthin and hypophyllanthin inhibit function of P-gp but not MRP2 in Caco-2 cells.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;65(2):292-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Agrimol B
Agrimol B is a main active ingredient isolated from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.
-
4-methoxylonchocarpi...
4-methoxylonchocarpin was isolated from the roots of Abrus precatorius as a potent anti-inflammatory compound.
-
Isosinomenina
Isotetrandrine is a bioactive component in Stephania tetrandra.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


