JOSAMYCIN
CAS No. 16846-24-5
JOSAMYCIN( EN-141 )
Catalog No. M20653 CAS No. 16846-24-5
JOSAMYCIN is a macrolide antibiotic exhibiting antimicrobial activity. The dissociation constant Kd from ribosome for Josamycin is 5.5 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 44 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 40 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 63 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 104 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 258 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameJOSAMYCIN
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionJOSAMYCIN is a macrolide antibiotic exhibiting antimicrobial activity. The dissociation constant Kd from ribosome for Josamycin is 5.5 nM.
-
DescriptionJOSAMYCIN is a macrolide antibiotic exhibiting antimicrobial activity. The dissociation constant Kd from ribosome for Josamycin is 5.5 nM.(In Vitro):Studies show that the average lifetime on the ribosome is 3 h for Josamycin and that the dissociation constants for Josamycin binding to the ribosome is 5.5 nM. Josamycin slows down formation of the first peptide bond of a nascent peptide in an amino acid-dependent way and completely inhibits formation of the second or third peptide bond, depending on peptide sequence at a saturating drug concentration, synthesis of fulllength proteins is completely shut down by Josamycin. At a saturating drug concentration, synthesis of fulllength proteins is completely shut down by Josamycin.(In Vivo):Blood and tissue levels of Josamycin after oral administration are 200 mg/kg to rabbits. Tissue levels are generally much higher than the blood levels, and 3 h after the administration, when the blood level is very low, the tissue levels are rather higher than those 1 h after the dose. One hour after the medication, the level in the lungs is the highest of all the tissue levels.
-
In VitroStudies show that the average lifetime on the ribosome is 3 h for Josamycin and that the dissociation constants for Josamycin binding to the ribosome is 5.5 nM. Josamycin slows down formation of the first peptide bond of a nascent peptide in an amino acid-dependent way and completely inhibits formation of the second or third peptide bond, depending on peptide sequence at a saturating drug concentration, synthesis of fulllength proteins is completely shut down by Josamycin. At a saturating drug concentration, synthesis of fulllength proteins is completely shut down by Josamycin.
-
In VivoBlood and tissue levels of Josamycin after oral administration are 200 mg/kg to rabbits. Tissue levels are generally much higher than the blood levels, and 3 h after the administration, when the blood level is very low, the tissue levels are rather higher than those 1 h after the dose. One hour after the medication, the level in the lungs is the highest of all the tissue levels.
-
SynonymsEN-141
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorBacterial
-
Research Area——
-
IndicationSuppurative streptococcus causes pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number16846-24-5
-
Formula Weight827.99
-
Molecular FormulaC42H69NO15
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:41.67 mg/mL (50.33 mM)
-
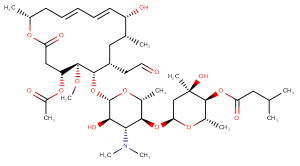
SMILESCO[C@H]1[C@@H](CC(=O)O[C@H](C)C\C=C\C=C\[C@H](O)[C@H](C)C[C@H](CC=O)[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@H]2C[C@@](C)(O)[C@@H](OC(=O)CC(C)C)[C@H](C)O2)[C@@H]([C@H]1O)N(C)C)OC(C)=O
-
Chemical NameLeucomycin V 3-acetate 4(sup B)-(3-methylbutanoate)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Eun-Young C So-Hui C Jin-Yi H et al. Josamycin suppresses Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide-induced production of nitric oxide and interleukin-1β in murine macrophages[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018 105:498-505.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin(MDL-63397, BI-397) is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal effect by disrupting cell wall biosynthesis.
-
Fenpropidin
Fenpropidin, a fungicide, is a specific inhibitor of sterol 14-reductase and biosynthesis.
-
Methyl α-D-mannopyra...
Methyl α-D-mannopyranoside can be used as an intermediate for chemical sythesis and can ?target macrophages in anti-tuberculosis inhalation therapy.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


