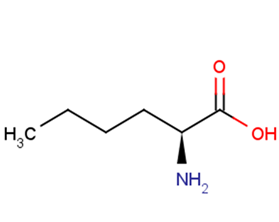
L-Norleucine
CAS No. 327-57-1
L-Norleucine( (S)-Norleucine | alpha-Aminocaproic acid | (S)-2-Aminohexanoic acid )
Catalog No. M19595 CAS No. 327-57-1
L-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine specifically affects protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and has antivirus activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Norleucine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine specifically affects protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and has antivirus activity.
-
DescriptionL-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine specifically affects protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and has antivirus activity.(In Vitro):L-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, specifically affecting protein synthesis in skeletal muscle. L-Norleucine has antiviral activity. L-Norleucine interacts with hnRNPA2/B1 protein to suppresses the expressions of Twist1 and Snail, two inhibitors of E-cadherin, and promotes the expression of E-cadherin, resulting in the inhibition of tumor metastasis.
-
In VitroL-Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, specifically affecting protein synthesis in skeletal muscle. L-Norleucine has antiviral activity. L-Norleucine interacts with hnRNPA2/B1 protein to suppresses the expressions of Twist1 and Snail, two inhibitors of E-cadherin, and promotes the expression of E-cadherin, resulting in the inhibition of tumor metastasis.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(S)-Norleucine | alpha-Aminocaproic acid | (S)-2-Aminohexanoic acid
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research AreaOthers
-
IndicationHot Flashes
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number327-57-1
-
Formula Weight131.17
-
Molecular FormulaC6H13NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM;Water: Soluble
-
SMILESCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Schott KJ et al. On the role of branched-chain amino acids in protein turnover of skeletal muscle. Studies in vivo with L-norleucine. Z Naturforsch C. 1985 May-Jun;40(5-6):427-37.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-Indoleacrylic acid
3-Indoleacrylic acid is a metabolite of tryptophan produced by Peptostreptococcus species. 3-Indoleacrylic acid has a beneficial effect on intestinal epithelial barrier function and mitigates inflammatory responses by immune cells.
-
Hydroxyphenylacetylg...
Hydroxyphenylacetylglycine (p-Hydroxyphenylacetylglycine) is an endogenous human metabolite.
-
Alloepipregnanolone
Alloepipregnanolone is a pregnane with anesthetic hypnotic and sedative properties.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


