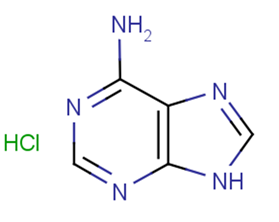
Adenine hydrochloride
CAS No. 2922-28-3
Adenine hydrochloride( Adenine hydrochloride | Leucon )
Catalog No. M18378 CAS No. 2922-28-3
Adenine HCl is a hydrochloride salt form of adenine which is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 28 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAdenine hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAdenine HCl is a hydrochloride salt form of adenine which is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry.
-
DescriptionAdenine hydrochloride.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAdenine hydrochloride | Leucon
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2922-28-3
-
Formula Weight171.59
-
Molecular FormulaC5H5N5·HCl
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (291.39 mM)
-
SMILESc1nc2c([nH]1)c(ncn2)N.Cl
-
Chemical Name1H-Purin-6-amine, monohydrochloride
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Silwal P, et al. Mol Immunol. 2015 Jun;65(2):242-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pseudolaric acid A-O...
Pseudolaric acid A-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside is a natural product with antibacterial, anticancer.
-
Dotinurad
Dotinurad is a potent agent of uricosuric (IC50: 3.6 μM for uric acid).
-
1-Isomangostin hydra...
1-Isomangostin is a natural product extracted from Garcinia mangostana. It has antifungal activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


