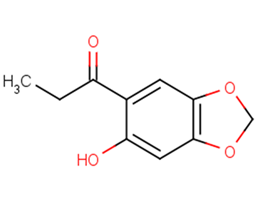
Kakuol
CAS No. 18607-90-4
Kakuol( —— )
Catalog No. M18150 CAS No. 18607-90-4
Kakuol has antifungal activity, it can completely inhibit the mycelial growth of Botrytis cinerea Pers ex Fr and Cladosporium cucumerinum Ellis & Arthur at 5 microg ml(-1) and 3 microg ml(-1), respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 76 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 93 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 160 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 232 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 343 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameKakuol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKakuol has antifungal activity, it can completely inhibit the mycelial growth of Botrytis cinerea Pers ex Fr and Cladosporium cucumerinum Ellis & Arthur at 5 microg ml(-1) and 3 microg ml(-1), respectively.
-
DescriptionKakuol has antifungal activity, it can completely inhibit the mycelial growth of Botrytis cinerea Pers ex Fr and Cladosporium cucumerinum Ellis & Arthur at 5 microg ml(-1) and 3 microg ml(-1), respectively. 2. kakuol and a derivative analogue are able to inhibit the DNA relaxation mediated by the human enzyme.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAntifungal
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number18607-90-4
-
Formula Weight194.18
-
Molecular FormulaC10H10O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (514.99 mM)
-
SMILESCCC(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C1O)OCO2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
WWL229
WWL229 is a selective inhibitor of Ces3.
-
CMPF
CMPF is a microtubule protein inhibitor that can be used to study tumors.
-
D-Proline
D-proline is an isomer of the naturally occurring amino acid L-Proline. D-amino acids have been found in relatively high abundance in human plasma and saliva. These amino acids may be of bacterial origin but there is also evidence that they are endogenously produced through amino acid racemase activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


