AG 1406
CAS No. 71308-34-4
AG 1406( —— )
Catalog No. M17575 CAS No. 71308-34-4
AG 1406 is a selective inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinase VEGF receptor 2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 75 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 36 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 57 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 85 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 259 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 384 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAG 1406
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAG 1406 is a selective inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinase VEGF receptor 2.
-
DescriptionAG 1406 is a selective inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinase VEGF receptor 2.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorVEGFR2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number71308-34-4
-
Formula Weight254.32
-
Molecular FormulaC16H18N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
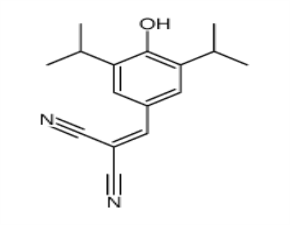
SMILESCC(C)c1cc(cc(c1O)C(C)C)C=C(C#N)C#N
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dihydrolycorine
Dihydrolycorine-HCL(DL) shows hypotensive effects, it can block alpha 1-adrenoceptors.
-
Urolithin C
Urolithin C is a gut metabolite of ellagic acid. Urolithin C induces apoptosis in PC12 cells through a mitochondria-mediated pathway.
-
Etalocib
Etalocib is a novel diaryl ether carboxylic acid derivative, is a selective and potent inhibitor of the lipoxygenase pathway either via antagonism of the leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptor or directly through 5'-lipoxygenase.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


