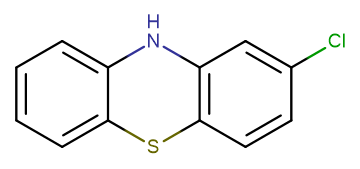
2-Chlorophenothiazine
CAS No. 92-39-7
2-Chlorophenothiazine( —— )
Catalog No. M16619 CAS No. 92-39-7
It is used as the intermediate of Chlorpromazine hydrochloride.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 51 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Chlorophenothiazine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIt is used as the intermediate of Chlorpromazine hydrochloride.
-
DescriptionIt is used as the intermediate of Chlorpromazine hydrochloride.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number92-39-7
-
Formula Weight233.72
-
Molecular FormulaC12H8ClNS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityLimited solubility
-
SMILESClC1=CC2=C(SC3=CC=CC=C3N2)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.el-Ezbawy SR, Alshaikh MA. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 1990;47(3):209-18.
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Hydroxybenzoyl cho...
4-Hydroxybenzoyl choline is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Fenchlorphos
Ronnel is a Filipino politician, entrepreneur, and businessman and a former councilor and currently serving as Mayor of General Santos.
-
Secoxyloganin methyl...
Dimethyl secologanoside (compound 2) is an e iridoid isolated from the leaves of Khaya senegalensis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


