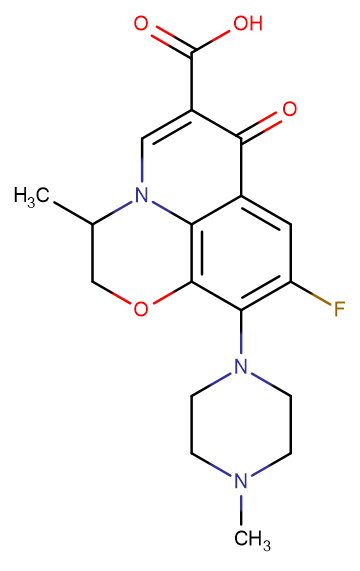
Ofloxacin
CAS No. 82419-36-1
Ofloxacin( DL-8280 | WP0405 )
Catalog No. M16061 CAS No. 82419-36-1
Ofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameOfloxacin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionOfloxacin is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase.
-
DescriptionOfloxacin is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase.(In Vitro):Ofloxacin (Hoe-280) is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase. In vitro it has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, although it is poorly active against anaerobes. Ofloxacin (Hoe-280), like other 4-quinolones, is unusual among front line drugs available to treat bacterial infections since it affects bacterial DNA synthesis, rather than cell wall or protein synthesis.(In Vivo):Ofloxacin (Hoe-280) (20 mg/kg), norfloxacin (40 mg/kg), pefloxacin mesylate dihydrate (40 mg/kg)and ciprofloxacin (50 mg/kg) are administered by gavage twice daily for three consecutive weeks. 6 weeks after treatment, the test animals are euthanised and Achilles tendon specimens are collected. A computer monitored tensile testing machine was utilised for biomechanical testing. The mean elastic modulus of the control group was significantly higher than that of the norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean yield force (YF) of the control group was significantly higher than those of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean ultimate tensile force (UTF) of the control group was significantly higher than of the ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). Hyaline degeneration and fibre disarrangement were observed in the tendons of the ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and ofloxacin treated-groups, whereas myxomatous degeneration was observed only in the ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin groups.
-
In VitroOfloxacin (Hoe-280) is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase. In vitro it has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, although it is poorly active against anaerobes. Ofloxacin (Hoe-280), like other 4-quinolones, is unusual among front line drugs available to treat bacterial infections since it affects bacterial DNA synthesis, rather than cell wall or protein synthesis.
-
In VivoOfloxacin (Hoe-280) (20 mg/kg), norfloxacin (40 mg/kg), pefloxacin mesylate dihydrate (40 mg/kg)and ciprofloxacin (50 mg/kg) are administered by gavage twice daily for three consecutive weeks. 6 weeks after treatment, the test animals are euthanised and Achilles tendon specimens are collected. A computer monitored tensile testing machine was utilised for biomechanical testing. The mean elastic modulus of the control group was significantly higher than that of the norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean yield force (YF) of the control group was significantly higher than those of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean ultimate tensile force (UTF) of the control group was significantly higher than of the ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). Hyaline degeneration and fibre disarrangement were observed in the tendons of the ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and ofloxacin treated-groups, whereas myxomatous degeneration was observed only in the ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin groups.
-
SynonymsDL-8280 | WP0405
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetTopoisomerase
-
RecptorTopo
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number82419-36-1
-
Formula Weight361.37
-
Molecular FormulaC18H20FN3O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 0.4 mg/mL (1.1 mM)
-
SMILESCC1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(=O)C3=CC(=C2N4CCN(CC4)C)F)C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-3,7-dihydro-2H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Divo AA, et al. Antimicrob Agents ChemOthers. 1988 Aug;32(8):1182-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SW-044248
SW-044248 is a novel selective inhibitor of Topoisomerase I; inhibits Top I differently from camptothecin.
-
Zoliflodacin
Zoliflodacin (ETX0914, AZD0914) is a new bacterial DNA gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitor. Zoliflodacin has potent in vitro antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, including S. aureus (MIC90: 0.25 μg/mL).
-
Heveaflavone
Heveaflavone has anti-proliferation effects, it shows moderate Topoisomerase I inhibitory activity. It also possesses a good antioxidant activity via its DPPH free radical scavenging.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


