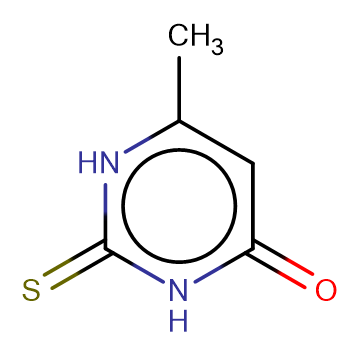
Methylthiouracil
CAS No. 56-04-2
Methylthiouracil( Alkiron, Antibason, Basecil, Basethyrin, Metacil, Methacil, Methylthiouracil )
Catalog No. M15041 CAS No. 56-04-2
A thiourea antithyroid agent that inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormone.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 36 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 116 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 36 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 116 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMethylthiouracil
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA thiourea antithyroid agent that inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormone.
-
DescriptionA thiourea antithyroid agent that inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormone. It is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.(In Vitro):HUVECs are treated with various concentrations of MTU (0-20 μM) for 6 h after the addition of LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4 h. MTU inhibits LPS-mediated hyperpermeability in endothelial cells, with the optimal effect occurring at a concentration above 5 μM. The effects of MTU are examined on HUVEC actin cytoskeletal arrangement by immunofluorescence staining of HUVEC monolayers with F-actin labeled fluorescein phalloidin. Control HUVECs exhibit a random distribution of F-actin throughout the cells, with some localization of actin filament bundles at the cell boundaries. Barrier disruption by LPS (100 ng/mL) is manifested by the formation of paracellular gaps in HUVECs. In addition, post-treatment with MTU (10 or 20 μM) results in inhibited formation of LPS-induced paracellular gaps with the formation of dense F-actin rings. To test the cytotoxicity of MTU, cellular viability assays are performed in HUVECs treated with MTU for 24 h. At concentrations up to 20 μM, MTU does not affect cell viability.
-
In VitroHUVECs are treated with various concentrations of MTU (0-20 μM) for 6 h after the addition of LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4 h. MTU inhibits LPS-mediated hyperpermeability in endothelial cells, with the optimal effect occurring at a concentration above 5 μM. The effects of MTU are examined on HUVEC actin cytoskeletal arrangement by immunofluorescence staining of HUVEC monolayers with F-actin labeled fluorescein phalloidin. Control HUVECs exhibit a random distribution of F-actin throughout the cells, with some localization of actin filament bundles at the cell boundaries. Barrier disruption by LPS (100 ng/mL) is manifested by the formation of paracellular gaps in HUVECs. In addition, post-treatment with MTU (10 or 20 μM) results in inhibited formation of LPS-induced paracellular gaps with the formation of dense F-actin rings. To test the cytotoxicity of MTU, cellular viability assays are performed in HUVECs treated with MTU for 24 h. At concentrations up to 20 μM, MTU does not affect cell viability.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAlkiron, Antibason, Basecil, Basethyrin, Metacil, Methacil, Methylthiouracil
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetAntiviral
-
Recptorantithyroid
-
Research AreaEndocrinology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number56-04-2
-
Formula Weight142.18
-
Molecular FormulaC5H6N2OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 28 mg/mL (196.93 mM)
-
SMILESc1(cc(=O)[nH]c(=S)[nH]1)C
-
Chemical Name4(1H)-Pyrimidinone, 2,3-dihydro-6-methyl-2-thioxo-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Vidarabine phosphate
Vidarabine phosphate is an adenosine monophosphate analog. It is the monophosphate ester of VIDARABINE. It also has antiviral and possibly antineoplastic properties.
-
Tenofovir exalidex
Tenofovir exalidex (CMX 157) is a lipid-conjugated acyclic nucleotide analog of Tenofovir, demonstrating efficacy against wild-type and antiretroviral-resistant HIV strains, including those resistant to multiple nucleoside/nucleotide analogs.
-
Azaribine
Azaribine (2;,3;,5;-Tri-O-acetyl-6-azauridine) is an orotate monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPD) inhibitor with broad-spectrum antiviral activity, inhibiting viral genome replication and gene transcription.Azaribine has been used in the study of Zika virus (ZIKV) infections, and in the study of psoriasis, arthritis and mycosis fungoides.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


