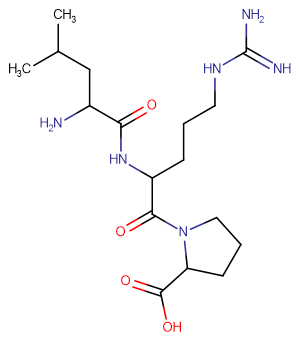
Leucylarginylproline
CAS No. 133943-59-6
Leucylarginylproline( —— )
Catalog No. M21019 CAS No. 133943-59-6
Leucylarginylproline is an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (IC50 : 0.27μM).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 308 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 462 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 686 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1017 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1377 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLeucylarginylproline
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLeucylarginylproline is an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (IC50 : 0.27μM).
-
DescriptionLeucylarginylproline is an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (IC50 : 0.27μM).
-
In VitroIntravenous injection of Leucylarginylproline (30mg/kg) causes a decrease in the blood pressure. The maximum mean blood pressure reduction (about 15 mmHg) occurrs about 2 min after the injection. Leucylarginylproline peptide reduces the blood pressure by about 15 mmHg at the fourth hour and shows a maximal reduction effect of about 35 mmHg at the eighth hour after oral administration.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
TargetRAAS
-
RecptorACE
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number133943-59-6
-
Formula Weight384.47
-
Molecular FormulaC17H32N6O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCC(C)CC(N)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Chen T L Lo Y C Hu W T et al. Microencapsulation and Modification of Synthetic Peptides of Food Proteins Reduces the Blood Pressure of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2003 51(6):1671-1675.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Leucylarginylproline
Leucylarginylproline is an?inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (IC50 : 0.27μM).
-
Delapril?Hydrochlori...
Delapril is a prodrug; it is converted into two active metabolites, 5-hydroxy delapril diacid and delapril diacid.
-
Vicenin -2
Vicenin 2 is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (IC50=43.83 μM) from the aerial parts of Desmodium styracifolium. Vicenin 2 is an inhibitor of α-glucosidase, PTP1B, and RLAR.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


