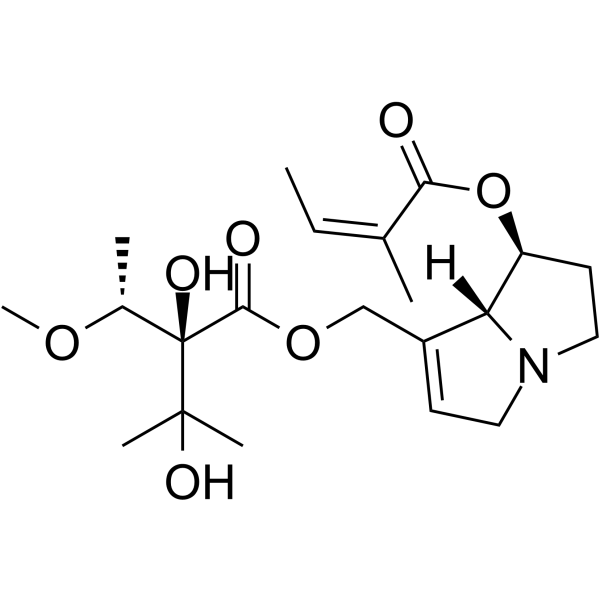
Lasiocarpine
CAS No. 303-34-4
Lasiocarpine( —— )
Catalog No. M31055 CAS No. 303-34-4
Lasiocarpine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid, it has acute cytotoxicity in human and hepatic cell lines.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 2137 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLasiocarpine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLasiocarpine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid, it has acute cytotoxicity in human and hepatic cell lines.
-
DescriptionLasiocarpine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid, it has acute cytotoxicity in human and hepatic cell lines.
-
In VitroLasiocarpine is toxic only after its metabolic conversion to the toxic intermediate, known as dehydrolasiocarpine.Dehydrolasiocarpine and other putative didehydropyrrolizidine alkaloids (the pyrrolic esters) are very reactive,they attack nucleophilic macromolecules such as DNA and proteins, eliciting severe toxicities, including liver veno-occlusive disease and tumors.Lasiocarpine is mainly metabolized in vitro through five metabolic pathways, dehydrogenation, ester bond cleavage, demethylation.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number303-34-4
-
Formula Weight411.49
-
Molecular FormulaC21H33NO7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ro 08-2750
Ro 08-2750 is a non-peptide and reversible nerve growth factor (NGF) inhibitor which binds to NGF, and with an IC50 of ~ 1 μM.
-
CJ-42794
CJ-42794 is a selective antagonist of prostaglandin E receptor subtype 4 (EP4). It inhibits [3H]-PGE2 binding to the human EP4 receptor (a mean pKi: 8.5).
-
Chetomin
Chetomin is an inhibitor of HIF-1 by weaken transcription of HIF-1, disrupting the binding of HIF-1α and HIF-2α to p300 at low nanomolar concentrations.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


