LDK1229
CAS No. 1800285-55-5
LDK1229( LDK 1229 )
Catalog No. M12734 CAS No. 1800285-55-5
LDK1229 is a novel potent, selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist with Ki of 220 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLDK1229
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLDK1229 is a novel potent, selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist with Ki of 220 nM.
-
DescriptionLDK1229 is a novel potent, selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist with Ki of 220 nM; exhibits 3-fold relative selectivity for the CB1 over CB2, exhibits efficacy comparable with SR141716A in antagonizing the basal G protein coupling activity of CB1; increases cell surface localization of CB1 and structurally distinct from the first-generation CB1 inverse agonists.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsLDK 1229
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetCannabinoid Receptor
-
RecptorCannabinoid Receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1800285-55-5
-
Formula Weight434.956
-
Molecular FormulaC24H29ClF2N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
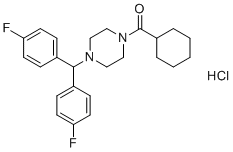
Chemical Name(4-(Bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)(cyclohexyl)methanone hydrochloride
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Mahmoud MM, et al. Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;87(2):197-206.
molnova catalog



related products
-
LDK1229
LDK1229 is a novel potent, selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist with Ki of 220 nM.
-
CB2R/FAAH modulator-...
CB2R/FAAH modulator-3 (compound 27) is a modulator targeting CB2R and FAAH, acting as a CB2R agonist with a Ki value of 20.1 nM and a CB1R agonist with a Ki value of 67.6 nM, while inhibiting FAAH with an IC50 value of 3.4 μM.
-
AM-1235
AM-1235 is a potent and selective cannabinoid receptor CB1 agonist.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


