KM02894
CAS No. 116850-74-9
KM02894( —— )
Catalog No. M36968 CAS No. 116850-74-9
KM02894 is a glutamate release inhibitor. Cancer cells release high levels of glutamate that can disrupt normal bone turnover, which can lead to cancer-induced bone pain.KM02894 may be used in the study of tumor-related diseases.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 39 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameKM02894
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKM02894 is a glutamate release inhibitor. Cancer cells release high levels of glutamate that can disrupt normal bone turnover, which can lead to cancer-induced bone pain.KM02894 may be used in the study of tumor-related diseases.
-
DescriptionKM02894 is an inhibitor of glutamate release. Cancer cells release high levels of glutamate, which disrupts normal bone turnover and may lead to cancer-induced bone pain. KM02894 can be used for cancer related research.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayNeuroscience
-
TargetGluR
-
RecptorGluR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number116850-74-9
-
Formula Weight215.3
-
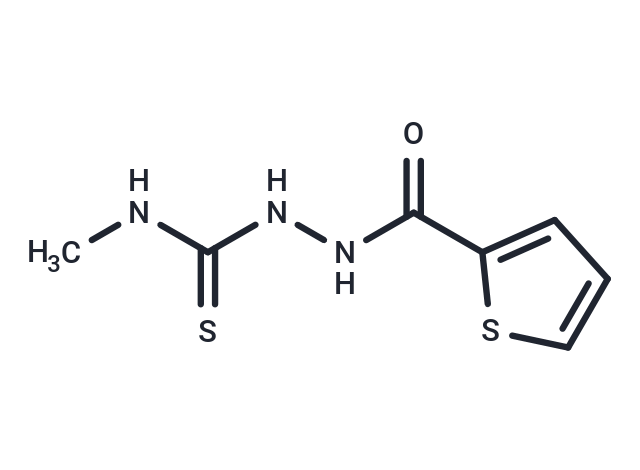
Molecular FormulaC7H9N3OS2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (154.81 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C)
-
SMILESCNC(=S)NNC(=O)C1=CC=CS1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Fazzari J, et.al. Inhibitors of glutamate release from breast cancer cells; new targets for cancer-induced bone-pain. Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 11;5:8380. ?
molnova catalog



related products
-
LY382884
LY382884 is a selective and potent GluR5 kainate receptor antagonist with anxiolytic activity.LY382884 blocks blockade of mossy fibre LTP induction.
-
Ziyuglycoside II
Ziyuglycoside II has anticancer, and antitumor properties against gastric cancer and breast cancer cells, by cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis.
-
TC-N 22A
TC-N 22A is a strong, selective, oral active mGlu4 forward allosteric regulator (PAM) that can cross the blood-brain barrier.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


