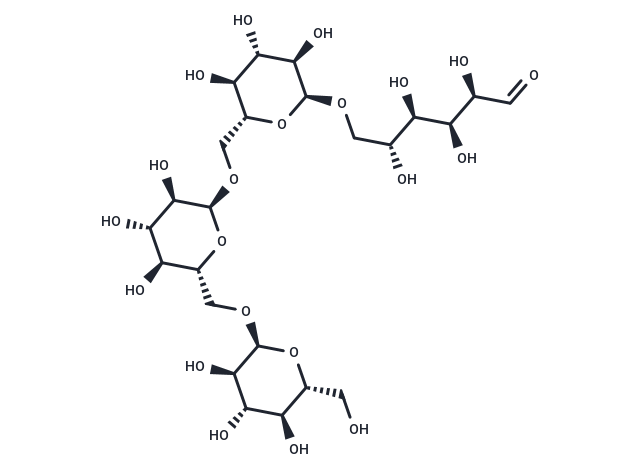
Isomaltotetraose
CAS No. 35997-20-7
Isomaltotetraose( —— )
Catalog No. M35210 CAS No. 35997-20-7
Isomaltotetraose (CI4) is a chained oligomeric isomaltose (IMO) present in syrups that induces dextranase synthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 46 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIsomaltotetraose
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIsomaltotetraose (CI4) is a chained oligomeric isomaltose (IMO) present in syrups that induces dextranase synthesis.
-
DescriptionIsomaltotetraose is one of isomalto-oligosaccharide (IMO), the main hydrolysis end products of DexKQ. Isomaltotetraose can induce dextranase synthesis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number35997-20-7
-
Formula Weight666.58
-
Molecular FormulaC24H42O21
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 250 mg/mL (375.05 mM; Ultrasonic)
-
SMILESO(C[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C=O)O)O)O)O)[C@H]1O[C@H](CO[C@H]2O[C@H](CO[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hongfei Liu, et al. Characterization of an Alkaline GH49 Dextranase from Marine Bacterium Arthrobacter oxydans KQ11 and Its Application in the Preparation of Isomalto-Oligosaccharide. Mar Drugs. 2019 Aug 19;17(8):479.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
(+)-Peusedanol
(+)-Peusedanol is a natural product isolated from Peucedanumjaponicum.
-
(R)-ZINC-3573
(R)-ZINC-3573 is a potent and highly selective MRGPRX2 probe that activates endogenous MRGPRX2 in a human mast cell line, inducing degranulation and calcium release.
-
Ganoderiol D
The fruit body of Ganoderma lucidum.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


