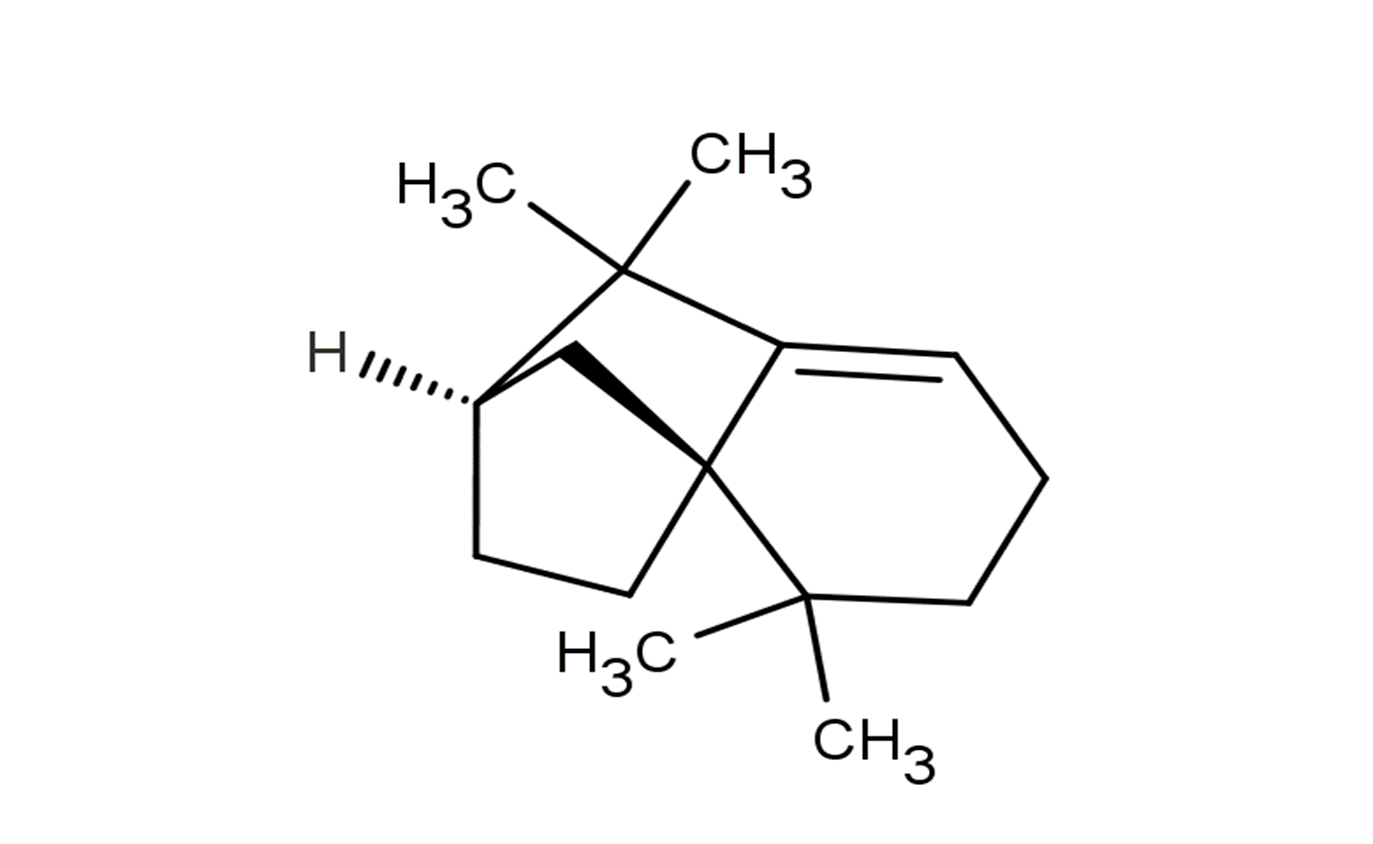
Isolongifolene
CAS No. 1135-66-6
Isolongifolene( (-)-Isolongifolene )
Catalog No. M23324 CAS No. 1135-66-6
Isolongifolene has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and neuroprotective properties.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 98 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 146 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 242 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 358 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIsolongifolene
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIsolongifolene has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and neuroprotective properties.
-
DescriptionIsolongifolene has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and neuroprotective properties. Isolongifolene is a tricyclic sesquiterpene isolated from Murraya koenigii. Isolongifolene attenuates Rotenone-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis through the regulation of P13K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathways.
-
In VitroIsolongifolene (0-50 μM; 26 hours; SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells) treatment significantly alleviates Rotenone-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells in a dose-dependent manner.Isolongifolene (10 μM; 26 hours; SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells) treatment attenuates Rotenone-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells.Isolongifolene (10 μM; 26 hours; SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells) treatment attenuates Rotenone induced toxicity by down-regulating Bax, caspases-3, 6, 8 and 9 expression and up-regulating of Bcl-2 expression. Furthermore regulation of p-P13K, p-AKT and p-GSK-3β expression by Isolongifolene. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells Concentration:0 μM, 1 μM, 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM and 50 μM Incubation Time:26 hours Result:Significantly alleviated Rotenone-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells.Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells Concentration:10 μMIncubation Time:26 hours Result:Attenuated Rotenone-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells.Western Blot AnalysisCell Line:SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells Concentration:10 μM Incubation Time:26 hours Result:Attenuated rotenone induced toxicity by down-regulatingBax, caspases-3, 6, 8 and 9 expression and up-regulating of Bcl-2 expression. Prevented the rotenone-induced decreased phosphorylation of GSK-3β.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(-)-Isolongifolene
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1135-66-6
-
Formula Weight204.35
-
Molecular FormulaC15H24
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESCC1(C)[C@]23CC[C@](C3)([H])C(C)(C)C2=CCC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Balakrishnan R, et al. Isolongifolene attenuates rotenone-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2018 Jan 1;10:248-261.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ticarcillin disodium
Ticarcillin disodium is an injectable antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-negative bacteria, particularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-
(Rac)-SHIN2
(Rac)-SHIN2, a serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) inhibitor, enhances NOTCH1-driven in vivo survival of primary T-ALL in mice and is useful for studying T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL).
-
ATMP
ATMP is a phosphonic acid with chelating properties. It is an antiscalant.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


