Iberverin
CAS No. 505-79-3
Iberverin( —— )
Catalog No. M21152 CAS No. 505-79-3
Iberverin is a naturan product. It induces phase II enzyme activity and decreases expression of androgen receptors in prostate cancer cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIberverin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIberverin is a naturan product. It induces phase II enzyme activity and decreases expression of androgen receptors in prostate cancer cells.
-
DescriptionIberverin is a naturan product. It induces phase II enzyme activity and decreases expression of androgen receptors in prostate cancer cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorothers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number505-79-3
-
Formula Weight147.26
-
Molecular FormulaC5H9NS2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
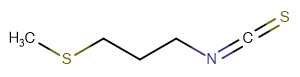
SMILESCSCCCN=C=S
-
Chemical Name(3-isothiocyanatopropyl)(methyl)sulfane
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Ernst I M A Palani K Esatbeyoglu T et al. Synthesis and Nrf2-inducing activity of the isothiocyanates iberverin iberin and cheirolin[J]. Pharmacological Research 2013 70(1):155-162.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Toosendanin
Toosendanin has effects on the growth, cell cycle arrest, induction of apoptosis and the involved signaling pathway in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-6 cells.
-
Fraxidin
Fraxidin is a class of coumarin. It is isolated from the roots of Jatropha podagrica.
-
Lanthanum trichlorid...
Lanthanum trichloride can be used as an analytical reagent and can be used as a raw material for extracting metal lanthanum and as a petroleum cracking catalyst.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


