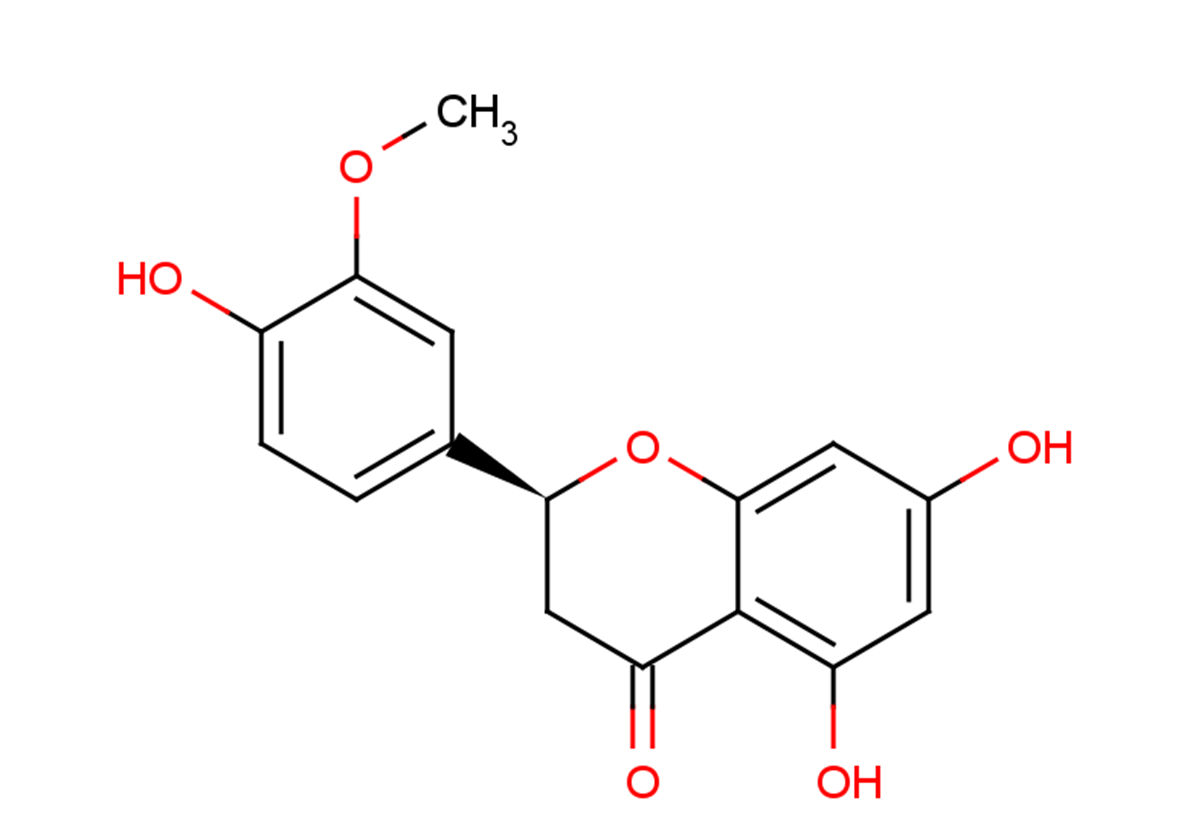
Homoeriodictyol
CAS No. 446-71-9
Homoeriodictyol( —— )
Catalog No. M22913 CAS No. 446-71-9
Homoeriodictyol, a naturally occurring, bitter-masking flavanone, as a promising agent to increase appetite and food intake. The flavanone homoeriodictyol can increase SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decrease serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.In contrast to other polyphenols, the flavanon Homoeriodictyol promotes glucose uptake by 29.0 ± 3.83% at a concentration of 100 μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHomoeriodictyol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHomoeriodictyol, a naturally occurring, bitter-masking flavanone, as a promising agent to increase appetite and food intake. The flavanone homoeriodictyol can increase SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decrease serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.In contrast to other polyphenols, the flavanon Homoeriodictyol promotes glucose uptake by 29.0 ± 3.83% at a concentration of 100 μM.
-
DescriptionHomoeriodictyol, a naturally occurring, bitter-masking flavanone, as a promising agent to increase appetite and food intake. The flavanone homoeriodictyol can increase SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decrease serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.In contrast to other polyphenols, the flavanon Homoeriodictyol promotes glucose uptake by 29.0 ± 3.83% at a concentration of 100 μM. The glucose uptake stimulating effect was sensitive to phloridzin, but not to phloretin, indicating an involvement of the sodium-coupled glucose transporter SGLT-1, but not of sodium-independent glucose transporters (GLUT). In addition, in contrast to the increased extracellular serotonin levels by stimulation with 500 mM D-(+)-glucose, treatment with 100 μM Homoeriodictyol decreased serotonin release by -48.8 ± 7.57% in Caco-2 cells via a phloridzin-sensitive signaling pathway. Extracellular serotonin levels were also reduced by -57.1 ± 5.43% after application of 0.01 μM Homoeriodictyol to human neural SH-SY5Y cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
Target5-HT Receptor
-
RecptorGLUT|5-HT Receptor|Sodium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number446-71-9
-
Formula Weight302.28
-
Molecular FormulaC16H14O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (165.41 mM)
-
SMILESO=C1C[C@@H](C2=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C2)OC3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C13
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.The flavanone homoeriodictyol increases SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decreases serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 13;12(2):e0171580.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SB 242084
SB 242084 is a potent, selective, brain penetrant 5-HT2C receptor antagonist.
-
Tropisetron
Tropisetron is an α7-nicotinic receptor agonist and 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with Kis of 6.9 nM and 5.3 nM, respectively.
-
Geissoschizine methy...
Geissoschizine methyl ether, a major indole alkaloid found in Uncaria hook, is a major active component of Yokukansan with psychotropic effects.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


