Felbamate
CAS No. 25451-15-4
Felbamate( ADD 03055 )
Catalog No. M13760 CAS No. 25451-15-4
Felbamate (FBM) is a potent nonsedative anticonvulsant whose clinical effect may be related to the inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 32 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 51 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 104 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 167 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 250 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 376 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFelbamate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFelbamate (FBM) is a potent nonsedative anticonvulsant whose clinical effect may be related to the inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA).
-
DescriptionFelbamate (FBM) is a potent nonsedative anticonvulsant whose clinical effect may be related to the inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) . Felbamate (Felbatol) is an anticonvulsant drug used in the treatment of epilepsy. Felbamate is used to control some types of seizures in the treatment of epilepsy. Felbamate acts on the central nervous system (CNS) to make it more difficult for seizures to start or to continue. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to use it. (In Vitro):Felbamate (W-554) is an anti-epileptic drug used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is used to treat partial seizures (with and without generalization) in adults and partial and generalized seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in children. However, an increased risk of potentially fatal aplastic anemia and/or liver failure limit the drugs usage to severe refractory epilepsy. Felbamate (W-554) has been proposed to a unique dual mechanism of action as a positive modulator of GABAA receptors and as a blocker of NMDA receptors, particularly isoforms containing the NR2B subunit. Although it is clear that felbamate does cause pharmacological inhibition of NMDA receptor of relevance of NMDA receptor blockade as a strategy for the treatment of human epilepsy has been questioned. Therefore, the importance of the effects of felbamate on NMDA receptors to its therapeutic action in epilepsy is uncertain.
-
In VitroFelbamate (W-554) is an anti-epileptic drug used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is used to treat partial seizures (with and without generalization) in adults and partial and generalized seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in children. However, an increased risk of potentially fatal aplastic anemia and/or liver failure limit the drugs usage to severe refractory epilepsy. Felbamate (W-554) has been proposed to a unique dual mechanism of action as a positive modulator of GABAA receptors and as a blocker of NMDA receptors, particularly isoforms containing the NR2B subunit. Although it is clear that felbamate does cause pharmacological inhibition of NMDA receptor of relevance of NMDA receptor blockade as a strategy for the treatment of human epilepsy has been questioned. Therefore, the importance of the effects of felbamate on NMDA receptors to its therapeutic action in epilepsy is uncertain.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsADD 03055
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetNMDAR
-
RecptorNMDA receptor
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number25451-15-4
-
Formula Weight238.24
-
Molecular FormulaC11H14N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 3 mg/mL (12.59 mM); DMSO: 48 mg/mL (201.47 mM)
-
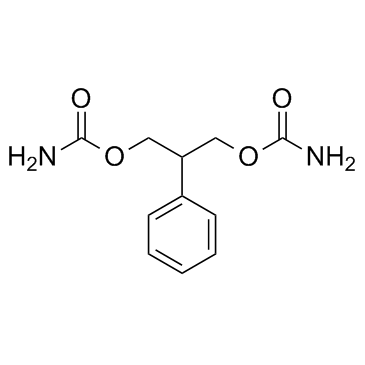
SMILESNC(OCC(C1=CC=CC=C1)COC(N)=O)=O
-
Chemical Name2-phenylpropane-1,3-diyl dicarbamate
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kuo CC, et al. Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Feb; 65(2):370-80.
molnova catalog



related products
-
D-AP5
D-AP5 is a NMDA receptor antagonist.
-
(R)-Serine
(R)-Serine is an endogenous amino acidis a potent co-agonist at the NMDA glutamate receptor.
-
1-Aminocyclobutaneca...
1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid is a NMDA receptor partial agonist. 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid act at the glycine site, NR1.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


