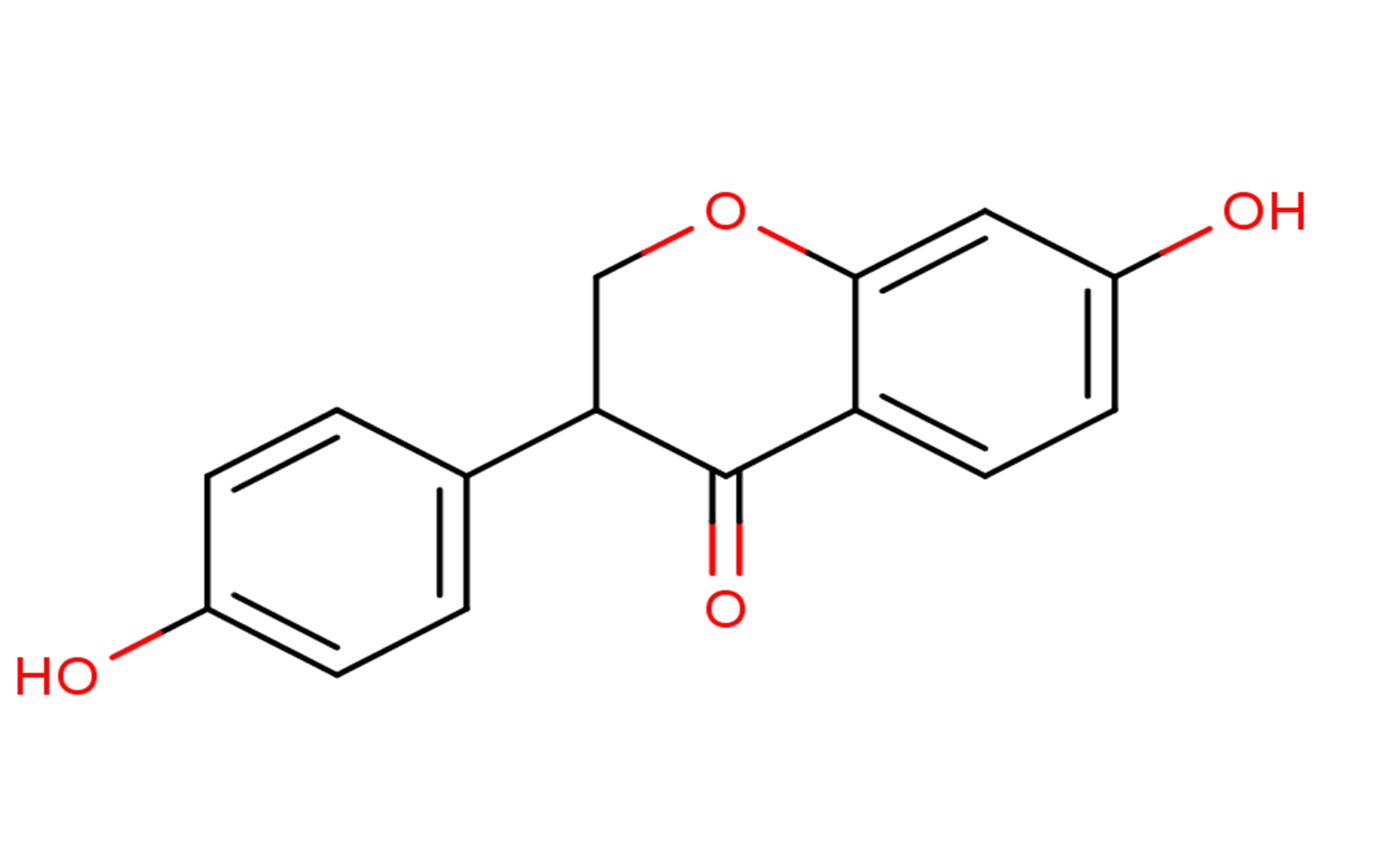
Dihydrodaidzein
CAS No. 17238-05-0
Dihydrodaidzein( (±)-Dihydrodaidzein )
Catalog No. M23777 CAS No. 17238-05-0
Dihydrodaidzein-producing bacteria might lead to clarification of some of the mechanisms regulating the production of equol by fecal microbiota.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 74 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydrodaidzein
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydrodaidzein-producing bacteria might lead to clarification of some of the mechanisms regulating the production of equol by fecal microbiota.
-
DescriptionDihydrodaidzein-producing bacteria might lead to clarification of some of the mechanisms regulating the production of equol by fecal microbiota.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(±)-Dihydrodaidzein
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17238-05-0
-
Formula Weight256.26
-
Molecular FormulaC15H12O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:100 mg/mL?(390.24 mM;?Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESO=C1C(C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)COC3=CC(O)=CC=C13
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Dihydrodaidzein-producing Clostridium-like intestinal bacterium, strain TM-40, affects in vitro metabolism of daidzein by fecal microbiota of human male equol producer and non-producers.Biosci Microflora. 2011;30(3):65-71.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Taurodeoxycholate so...
Taurodeoxycholate sodium salt is a bile salt-related anionic detergent used for isolation of membrane proteins including inner mitochondrial membrane proteins. and it inhibits various inflammatory responses
-
N-Acetylputrescine h...
N-Acetylputrescine is a polyamine commonly occurring excreted in normal human urine.
-
cis-4-Hydroxy-L-prol...
cis-4-Hydroxy-L-proline is an inhibitor of the synthesis and extracellular deposition of collagen. cis-4-Hydroxy-L-proline could inhibit fibroblast growth by preventing the deposition of triple-helical collagen on the cell layer.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


