Diflunisal
CAS No. 22494-42-4
Diflunisal( 5-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)salicylic Acid | MK-647 )
Catalog No. M13615 CAS No. 22494-42-4
Diflunisal, a salicylate derivative, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) with pharmacologic actions similar to other prototypical NSAIAs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 80 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 133 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDiflunisal
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDiflunisal, a salicylate derivative, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) with pharmacologic actions similar to other prototypical NSAIAs.
-
DescriptionDiflunisal, a salicylate derivative, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) with pharmacologic actions similar to other prototypical NSAIAs. Diflunisal possesses anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity. Though its mechanism of action has not been clearly established, most of its actions appear to be associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis via the arachidonic acid pathway. Diflunisal is used to relieve pain accompanied with inflammation and in the symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. .(In Vivo):Administration of increasing doses of Diflunisal to rats shows that the effect of the dose on the pharmacokinetics of Diflunisal is quite complicated. The plasma concentrations of Diflunisal decline exponentially with time, albeit with a half-life that increases with increasing dose. The CLP is reduced considerably when the dose increases from 3 to 10 mg/kg and then remains relatively constant over the dose range of 10 to 60 mg/kg. Diflunisal has been shown to be highly bound to rat plasma protein and dependent on concentration. The fraction of unbound Diflunisal is increased about 10-fold over the concentration range of 5 to 300 μg/mL. Diflunisal exhibits activity after oral administration with potency about 25 times greater than that of aspirin, about 3 times that of glafenine and twice that of zomepirac.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoAdministration of increasing doses of Diflunisal to rats shows that the effect of the dose on the pharmacokinetics of Diflunisal is quite complicated. The plasma concentrations of Diflunisal decline exponentially with time, albeit with a half-life that increases with increasing dose. The CLP is reduced considerably when the dose increases from 3 to 10 mg/kg and then remains relatively constant over the dose range of 10 to 60 mg/kg. Diflunisal has been shown to be highly bound to rat plasma protein and dependent on concentration. The fraction of unbound Diflunisal is increased about 10-fold over the concentration range of 5 to 300 μg/mL. Diflunisal exhibits activity after oral administration with potency about 25 times greater than that of aspirin, about 3 times that of glafenine and twice that of zomepirac.
-
Synonyms5-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)salicylic Acid | MK-647
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
Recptorp300
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number22494-42-4
-
Formula Weight250.2
-
Molecular FormulaC13H8F2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
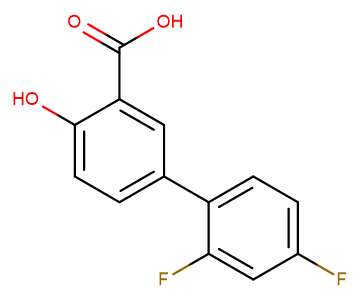
SMILESO=C(C1=CC(C2=CC=C(F)C=C2F)=CC=C1O)O
-
Chemical Name2',4'-difluoro-4-hydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Jeske AH. J Gt Houst Dent Soc. 1999, 71(4):39-40.
molnova catalog



related products
-
ZL0590
ZL0590 is an effective and selective inhibitor of BD1-BRD4 (IC50 = 90 nM) with anti-inflammatory activities.
-
PBRM1-BD2-IN-3
PBRM1-BD2-IN-3 (compound 12) is a potent PBRM1-BD2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 1.1 μM, used in anticancer research.
-
TRIM24/BRPF1-IN-2
TRIM24/BRPF1-IN-2 is a selective dual TRIM24/BRPF1 inhibitor with anticancer activity that inhibits proliferation, gene and protein expression, and colony formation of prostate cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


