DRB
CAS No. 53-85-0
DRB( —— )
Catalog No. M21065 CAS No. 53-85-0
DRB is a nucleoside analog that inhibits several carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) kinases including casein kinase II (IC50 range of 4-10 μM).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 65 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 87 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 140 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDRB
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDRB is a nucleoside analog that inhibits several carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) kinases including casein kinase II (IC50 range of 4-10 μM).
-
DescriptionDRB is a nucleoside analog that inhibits several carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) kinases including casein kinase II (IC50 range of 4-10 μM).
-
In VitroWestern Blot Analysis Cell Line:LS174T, HT29, SW48 Concentration:80 μg/mL Incubation Time:24 h Result:Decreased incorporation of [5,6-3H] uridine and increased level of p53 protein.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:MCF-7, T-47D Concentration:10, 50, 75,100 μM Incubation Time:72 h Result:Inhibited cell-growth in a dose-dependent manner.Resulted in a higher early apoptotic population (5.7 ± 1.1 vs. 2 ± 0.4%) and late apoptotic population (15.9 ± 2.4 vs. 7.7 ± 0.9%) at a concentration of 75 μM.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:MCF-7 Concentration:75 μM Incubation Time:0.5, 2, 6, 10 h Result:Reduced Mcl-1 protein levels in a time-dependent manner and increased the level of p53 after 6 h.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetHIV
-
RecptorHIV
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number53-85-0
-
Formula Weight319.14
-
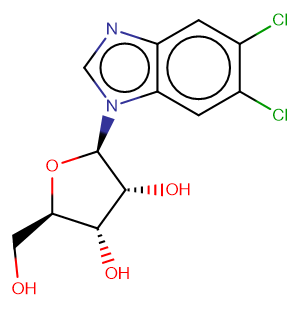
Molecular FormulaC12H12Cl2N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (313.34 mM)
-
SMILESOC[C@H]1O[C@@H](n2cnc3cc(Cl)c(Cl)cc32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Marciniak R A Sharp P A . HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes.[J]. Embo Journal 1991 10(13):4189-4196.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(S)-(+)-N-3-Benzylni...
(S)-(+)-N-3-Benzylnirvanol is a cytochrome P450 CYP2C19 inhibitor with a ki value of 82.5μM for CYP2C9 and 0.25μM for CYP2C19, which can be used to study HIV infection.
-
ANTHRAQUINONE-2-CARB...
Anthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid acts as a potent anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive component in vivo, thus contributing to the immune regulatory role of fruits and herbs.
-
Feruloyltyramine
NTF is likely to inhibit COX enzymes, thereby suppressing P-selectin expression on platelets, is a platelet aggregation inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


