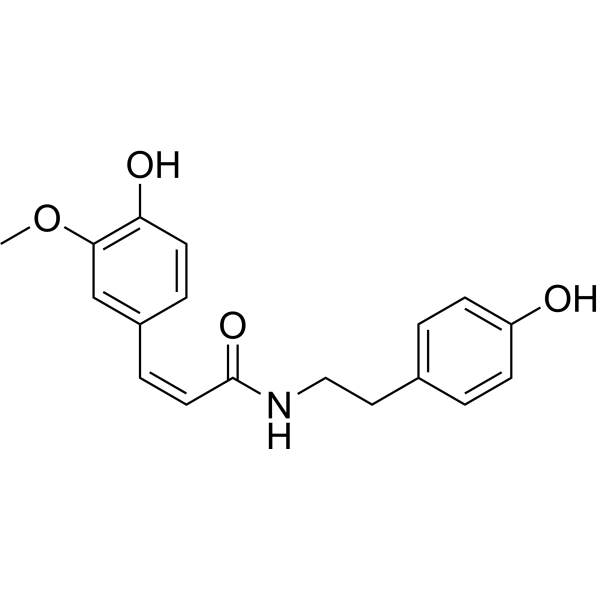
Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine
CAS No. 80510-09-4
Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine( —— )
Catalog No. M31341 CAS No. 80510-09-4
Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is a naturally occurring compound found in various plants that shows cytotoxicity against the P-388 cancer cell line. Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is an inhibitor of in vitro prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 285 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 426 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCis-N-Feruloyltyramine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCis-N-Feruloyltyramine is a naturally occurring compound found in various plants that shows cytotoxicity against the P-388 cancer cell line. Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is an inhibitor of in vitro prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.
-
DescriptionCis-N-Feruloyltyramine is a naturally occurring compound found in various plants that shows cytotoxicity against the P-388 cancer cell line. Cis-N-Feruloyltyramine is an inhibitor of in vitro prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number80510-09-4
-
Formula Weight313.4
-
Molecular FormulaC18H19NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Fluorogestone acetat...
Fluorogestone acetate showed a high potency with short duration of activity and performed physiologically similar to progesterone. FGA was approximately 20 - 25 times more potent than progesterone.
-
Methyloleoside
Methyloleoside is a natural product.
-
Metyrapone
Metyrapone is an inhibitor of cytochrome P450-mediated ω/ω-1 hydroxylase activity and CYP11B1.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


