CPSI-1306
CAS No. 1309793-47-2
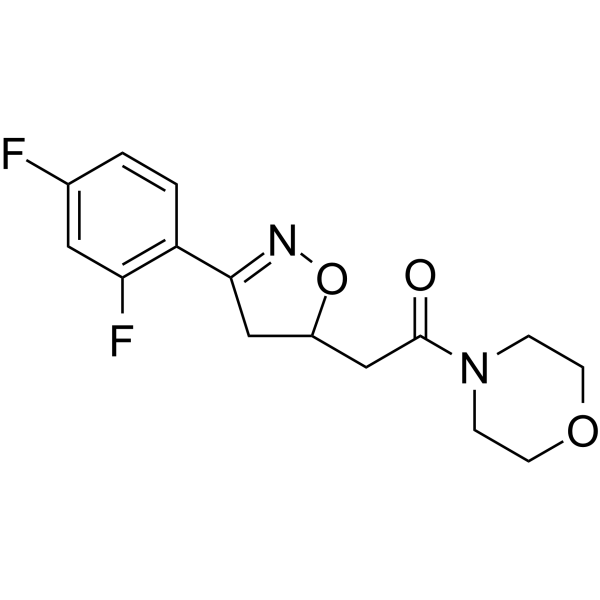
CPSI-1306( cpsi-1306 | 2-(3-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-5-yl)-1-morpholinoethan-1-one )
Catalog No. M26869 CAS No. 1309793-47-2
(±)-CPSI-1306 is a macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) antagonist and can be used in studies about non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and the prevention of the deleterious cutaneous effects of acute and chronic UVB exposure.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 41 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 74 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 133 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 241 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 329 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCPSI-1306
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(±)-CPSI-1306 is a macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) antagonist and can be used in studies about non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and the prevention of the deleterious cutaneous effects of acute and chronic UVB exposure.
-
Description(±)-CPSI-1306 is a macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) antagonist and can be used in studies about non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and the prevention of the deleterious cutaneous effects of acute and chronic UVB exposure.(In Vivo):In mice, (±)-CPSI-1306 decreases their blood glucose levels and can be effective in treating non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) as characterized by high serum levels of glucose and inflammatory cytokine. (±)-CPSI-1306-induced keratinocyte apoptosis is appreciated 30 minutes after a single UVB exposure. (±)-CPSI-1306-treated mice show a significant increase in expression of cleaved caspase-3 at 6, 24, and 48 hours following UVB exposure. (±)-CPSI-1306 reduces acute UVB-induced keratinocyte DNA damage and UVB-induced acute inflammation.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoMice treated with CPSI-1306 show a significant drop in their blood glucose levels, which is associated with a reduction in serum levels of inflammatory cytokines. As expected, control mice treated with vehicle develop NIDDM as characterized by high serum levels of glucose and inflammatory cytokine. Furthermore, they also show that orally bioavailable CPSI-1306 can be effective in treating this disease. CPSI-1306-induced keratinocyte apoptosis could be appreciated as early as 30 minutes after a single UVB exposure. At 6, 24, and 48 hours following UVB exposure, the CPSI-1306-treated mice show significantly increased expression of cleaved caspase-3 compared with the vehicle-treated mice. CPSI-1306 reduces acute UVB-induced keratinocyte DNA damage and UVB-induced acute inflammation.
-
Synonymscpsi-1306 | 2-(3-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-5-yl)-1-morpholinoethan-1-one
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAddAB helicase-nuclease| RecBCD helicase-nuclease
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1309793-47-2
-
Formula Weight310.301
-
Molecular FormulaC15H16F2N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 6 mg/mL (19.34 mM)
-
SMILESFc1ccc(C2=NOC(CC(=O)N3CCOCC3)C2)c(F)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Bannister TD, et al. ML328: A Novel Dual Inhibitor of Bacterial AddAB and RecBCD Helicase-nuclease DNA Repair Enzymes. 2012 Dec 17 [updated 2013 Apr 5]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet].
molnova catalog



related products
-
Baimantuoluoside C
12-Deoxywithastramonolide is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Fluocinolone acetoni...
Fluocinolone Acetonide is a corticosteroid that binds to the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor.
-
[D-Pro2,D-Trp6,8,Nle...
(D-Pro2,D-Trp6,8,Nle10)-Neurokinin B is a competitive antagonist of Neurokinin B (Neurokinin Receptor) with a pA2 of 5.5. (D-Pro2,D-Trp6,8,Nle10)-Neurokinin B shows no influence on Substance P or Neurokinin A.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


