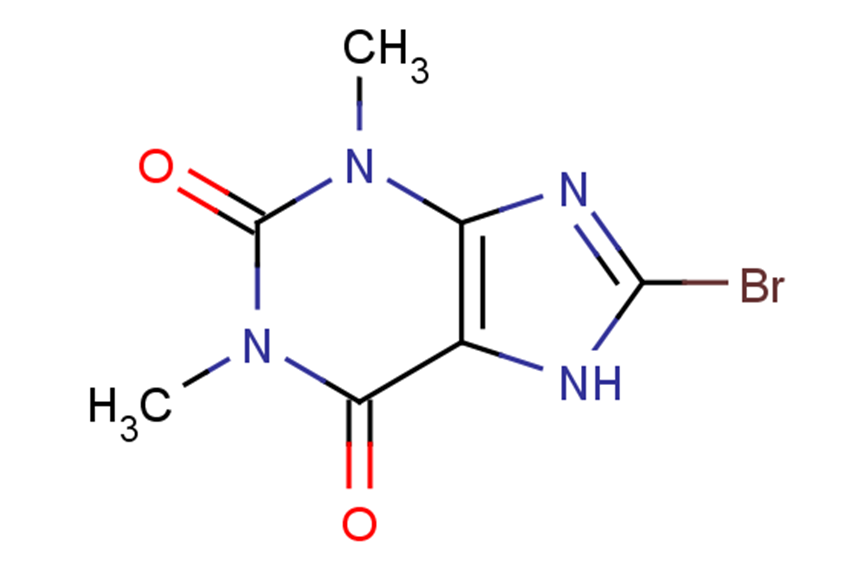
Bromotheophylline
CAS No. 10381-75-6
Bromotheophylline( 8-BROMOTHEOPHYLLINE )
Catalog No. M22265 CAS No. 10381-75-6
Bromotheophylline is the active moiety of pamabrom, a mixture of 2-amino-2-methyl-propanol and bromotheophylline.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBromotheophylline
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBromotheophylline is the active moiety of pamabrom, a mixture of 2-amino-2-methyl-propanol and bromotheophylline.
-
DescriptionBromotheophylline is the active moiety of pamabrom, a mixture of 2-amino-2-methyl-propanol and bromotheophylline. From this mixture, bromotheophylline acts as a weak diuretic that has been used along with some analgesics to relieve the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms8-BROMOTHEOPHYLLINE
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number10381-75-6
-
Formula Weight259.06
-
Molecular FormulaC7H7BrN4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (96.50 mM)
-
SMILESCn2c(=O)n(C)c1nc([Br])nc1c2=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Samura B A . [Effect of imidazo(1,2-f)xanthine derivatives on cerebral cortical bioelectrical activity and evoked potentials][J]. Farmakologiia i toksikologiia, 1983, 46(1):17-20.
molnova catalog



related products
-
14-Dichlorobenzene
14-Dichlorobenzene is a disinfectant pesticide and deodorant.
-
Gossypetin 3-sophoro...
The herbs of Abelmoschus manihot.
-
Safflower yellow
Safflower yellow is extracted from the flowers of the plant safflower (Carthamus tinctorius).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


