Batabulin
CAS No. 195533-53-0
Batabulin( T138067 )
Catalog No. M23886 CAS No. 195533-53-0
Batabulin is an antitumor compound, which binds covalently and selectively to a subset of the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 160 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 282 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 417 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 601 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1242 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBatabulin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBatabulin is an antitumor compound, which binds covalently and selectively to a subset of the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization.
-
DescriptionBatabulin is an antitumor compound, which binds covalently and selectively to a subset of the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization. Batabulin affects cell morphology and leads to cell-cycle arrest ultimately induce apoptotic cell death.
-
In VitroCell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:MCF7 cells Concentration:30 nM, 100 nM and 300 nM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Showed an arrest at the G2/M cell-cycle boundary.Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:MCF7 cells Concentration:30 nM, 100 nM and 300 nM Incubation Time:24 hours or 48 hours Result:25-30% of cells showed the reduced DNA content characteristic of apoptotic cells.
-
In VivoAnimal Model:Male athymic nude mice (nu/nu) (6-8 week-old, 20-25 g) injected with CCRF-CEM cells Dosage:40 mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; once per week; on days 5, 12, and 19 Result:Impaired the growth of the drug-sensitive CCRF-CEM tumors.
-
SynonymsT138067
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorApoptosis|Tubulin β
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number195533-53-0
-
Formula Weight371.26
-
Molecular FormulaC13H7F6NO3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:100 mg/mL (269.35 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
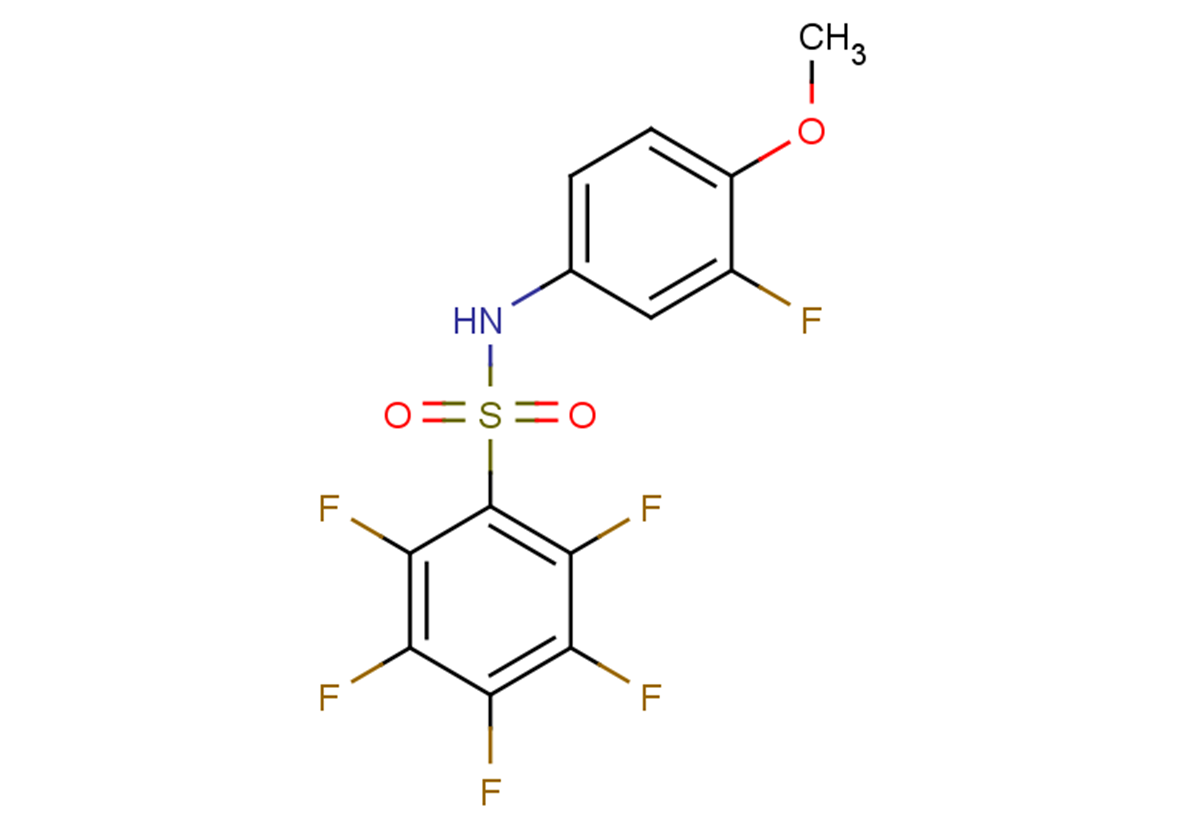
SMILESO=S(C1=C(F)C(F)=C(F)C(F)=C1F)(NC2=CC=C(OC)C(F)=C2)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Shan B, et al. Selective, covalent modification of beta-tubulin residue Cys-239 by T138067, an antitumor agent with in vivo efficacy against multidrug-resistant tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 May 11;96(10):5686-91.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Batabulin
Batabulin is an antitumor compound, which binds covalently and selectively to a subset of the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization.
-
CP 461
CP 461 (UNII-68OJX9I7DT), a specific PDE2A inhibitor, is a novel pro-apoptotic compound that inhibits cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase but not cyclooxygenase-1 or -2.
-
BFC1108
BFC1108 targets Bcl-2 and converts it to a pro-apoptotic protein, inhibits the growth of triple-negative breast cancer xenografts with high Bcl-2 expression, inhibits breast cancer lung metastasis, and induces apoptosis of Bcl-2-expressing cancer cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


