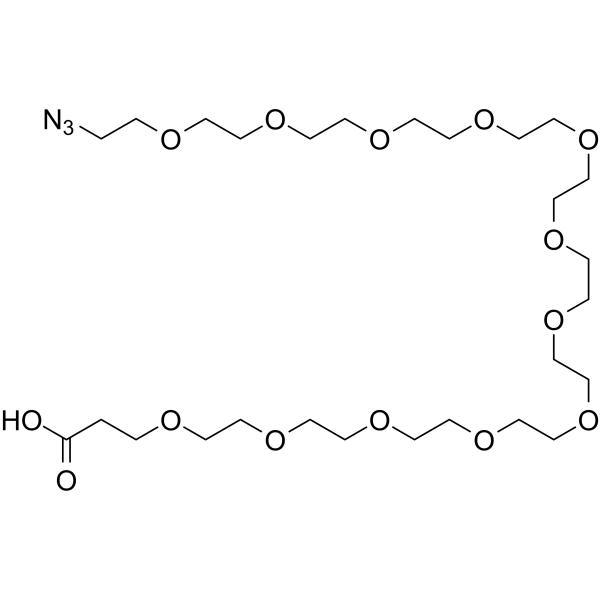
Azido-PEG12-acid
CAS No. 2152679-71-3
Azido-PEG12-acid( —— )
Catalog No. M26893 CAS No. 2152679-71-3
Azido-PEG12-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 52 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAzido-PEG12-acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAzido-PEG12-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
DescriptionAzido-PEG12-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.(In Vitro):PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In VitroPROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorflap endonuclease 1 (FEN1)
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2152679-71-3
-
Formula Weight643.728
-
Molecular FormulaC27H53N3O14
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOC(=O)CCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Application of small-molecular inhibitor SC13 targeting to FEN1 and derivative of small-molecular inhibitor SC13 in preparing tumor treatment medicine. CN106692155A.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ampelopsin G
Ampelopsin G is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Azvudine hydrochlori...
Azvudine hydrochloride (RO-0622) is a potent nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) with strong antiviral effects against HIV, HBV, and HCV.
-
8-Geranyloxy-5,7-dim...
8-Geranyloxy-5,7-dimethoxycoumarin is a natural product of Toddalia, Rutaceae. The catalog number is TN3277 and the CAS number is 1228175-65-2. 8-Geranyloxy-5,7-dimethoxycoumarin can be used as a reference standard.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


