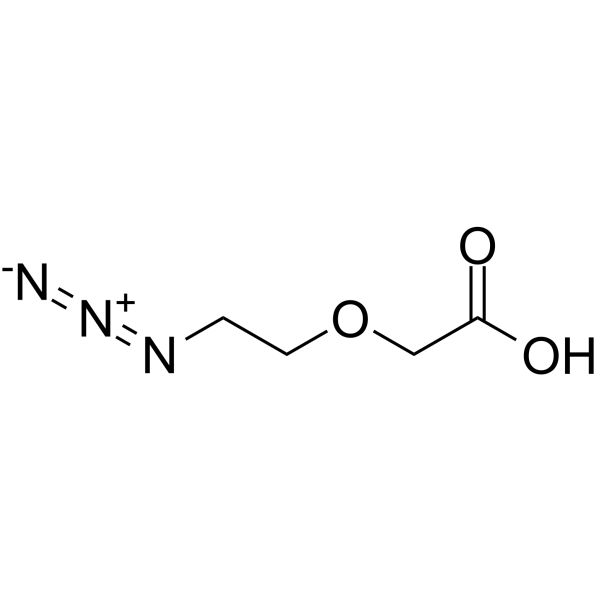
Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H
CAS No. 79598-48-4
Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H( 2-(2-azidoethoxy)acetic acid )
Catalog No. M26623 CAS No. 79598-48-4
Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H is a PROTAC linker that refers to an alkyl/ether combination. Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H can be used to synthesize PROTAC BRD4 Degrader-1.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAzido-PEG1-CH2CO2H
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAzido-PEG1-CH2CO2H is a PROTAC linker that refers to an alkyl/ether combination. Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H can be used to synthesize PROTAC BRD4 Degrader-1.
-
DescriptionAzido-PEG1-CH2CO2H is a PROTAC linker that refers to an alkyl/ether combination. Azido-PEG1-CH2CO2H can be used to synthesize PROTAC BRD4 Degrader-1.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms2-(2-azidoethoxy)acetic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number79598-48-4
-
Formula Weight145.118
-
Molecular FormulaC4H7N3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (344.54 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)COCCN=[N+]=[N-]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Baudouin G,et al. Lugrandoside: a new phenylpropanoid glycoside from various digitalis species. Planta Med. 1988 Aug;54(4):321-3.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Thiazolyl blue tetra...
Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide(MTT).
-
Chamigrenol
Chamigrenol is a promising candidate for the development of potent Na+/K+ ATPase inhibitors and antimicrobial agents.
-
Trachelanthine
Trachelanthine is a natural product from Eupatorium fortunei.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


