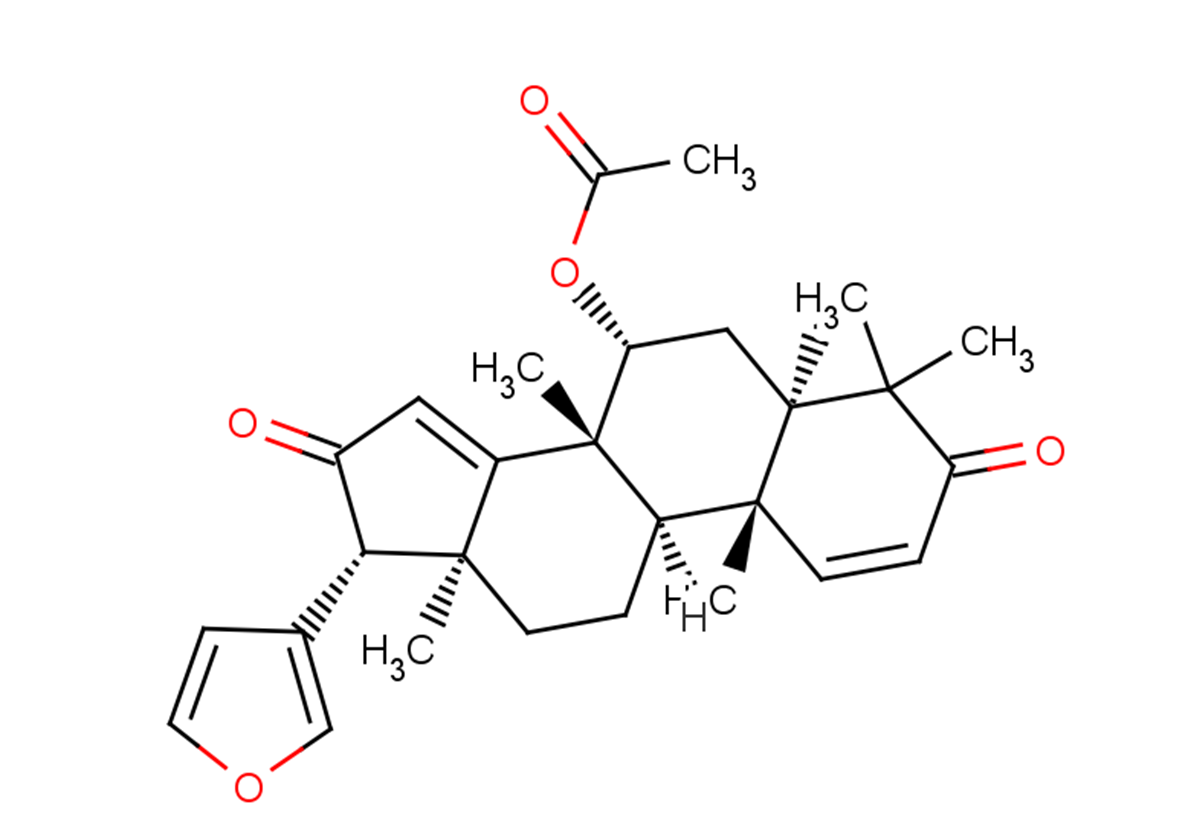
Azadiradione
CAS No. 26241-51-0
Azadiradione( AZD )
Catalog No. M24172 CAS No. 26241-51-0
Azadiradione (AZD) from the methanolic extract of seeds of Azadirachta indica.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 272 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 489 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 735 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1017 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1377 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAzadiradione
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAzadiradione (AZD) from the methanolic extract of seeds of Azadirachta indica.
-
DescriptionAzadiradione (AZD) from the methanolic extract of seeds of Azadirachta indica.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAZD
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number26241-51-0
-
Formula Weight450.57
-
Molecular FormulaC28H34O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC[C@@]1(C([C@]2(C)[C@H](OC(C)=O)C[C@@]3([H])C(C)(C)C(C=C[C@]3(C)[C@@]2([H])CC1)=O)=C4)[C@H](C5=COC=C5)C4=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Nelson V K , Ali A , Dutta N , et al. Azadiradione ameliorates polyglutamine expansion disease in Drosophila by potentiating DNA binding activity of heat shock factor 1[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(48):78281-78296.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dotinurad
Dotinurad is a potent agent of uricosuric (IC50: 3.6 μM for uric acid).
-
Bacitracin
Bacitracin is a mixture of related cyclic polypeptides produced by organisms of the licheniformis group of Bacillus subtilis var Tracy.
-
Cryptating agent 222
Cryptating agent 222 is a cryptand used with potassium mirror to reduce a hindered distannene to a crystalline radical anion and forms ligands with metal cations.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


