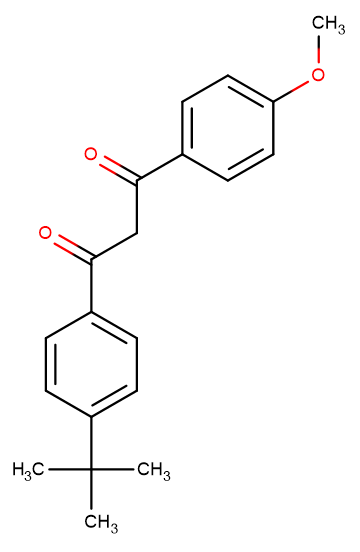
Avobenzone
CAS No. 70356-09-1
Avobenzone( BMDBM | Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane )
Catalog No. M15703 CAS No. 70356-09-1
Avobenzone is an oil soluble ingredient used in sunscreen products to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays and a dibenzoylmethane derivative.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAvobenzone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAvobenzone is an oil soluble ingredient used in sunscreen products to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays and a dibenzoylmethane derivative.
-
DescriptionAvobenzone is an oil soluble ingredient used in sunscreen products to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays and a dibenzoylmethane derivative.
-
In VitroAvobenzone (EC50=14.1 μM) significantly promots adipogenesis in hBM-MSCs as its positive control obesogenic chemicals. Avobenzone (10 μM) significantly up-regulates mRNA levels of PPARγ during adipogenesis in hBM-MSCs.Avobenzone (1-50 μM; 48 hours) inhibits proliferative activities of human trophoblast cells.Avobenzone (1-50 μM; 48 hours) induces apoptosis in HTR8/SVneo cells.Avobenzone only shows weak ERa agonism and weak AR antagonism. Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:HTR8/SVneo cells Concentration:1-50 μM Incubation Time:48 hours Result:Inhibited proliferative activities of HTR8/SVneo cells.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBMDBM | Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number70356-09-1
-
Formula Weight310.39
-
Molecular FormulaC20H22O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 9 mg/mL (28.99 mM); DMSO: 62 mg/mL (199.74 mM)
-
SMILESO=C(C1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1)CC(C2=CC=C(OC)C=C2)=O
-
Chemical Name1-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-dione
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Dunkelberger AD, et al. J Phys Chem A. 2015 Jun 2.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nicarbazin
Nicarbazin is an equimolar complex of 4,4'-Dinitrocarbanilide and 2-Hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine.
-
Maleimide
Maleimide (25-Pyrroledone) is a new nanoparticle surface functional group which favors easy conjugation with cell penetration peptides. The conjugation is enabled via click chemistry to preserve its biofunctions.
-
LICOCHALCONEC
Licochalcone C has potent antioxidant properties and inhibition of bacterial growth and cellular respiration.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


