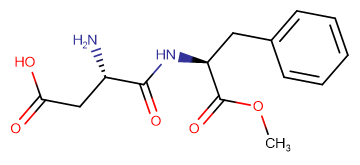
Aspartame
CAS No. 22839-47-0
Aspartame( L-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine methyl ester )
Catalog No. M13628 CAS No. 22839-47-0
Aspartame is an artificial, non-saccharide sweetener used as a sugar substitute in some foods and beverages.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 56 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAspartame
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAspartame is an artificial, non-saccharide sweetener used as a sugar substitute in some foods and beverages.
-
DescriptionAspartame is an artificial, non-saccharide sweetener used as a sugar substitute in some foods and beverages.(In Vitro):Aspartame is composed of phenylalanine (an important role in neurotransmitter regulation), aspartic acid (an excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system) and methanol.(In Vivo):Aspartame (4000 mg/kg bw/day; p.o.) shows no adverse effect in acute, subacute and chronic toxicity studies with aspartame, and its decomposition products, conducted in mice, rats, hamsters and dogs.
-
In VitroAspartame is composed of phenylalanine (an important role in neurotransmitter regulation), aspartic acid (an excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system) and methanol.
-
In VivoAspartame (4000 mg/kg bw/day; p.o.) shows no adverse effect in acute, subacute and chronic toxicity studies with aspartame, and its decomposition products, conducted in mice, rats, hamsters and dogs.
-
SynonymsL-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine methyl ester
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorTaste receptor| Transient receptor potential cation channel
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number22839-47-0
-
Formula Weight294.3
-
Molecular FormulaC14H18N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 4 mg/mL (13.59 mM); DMSO: 33 mg/mL (112.13 mM)
-
SMILESO=C(O)C[C@H](N)C(N[C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(OC)=O)=O
-
Chemical Name(3S)-3-Amino-4-[[(2S)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Xu H, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 28;101(39):14258-63.
molnova catalog



related products
-
P61 (343 - 355), M. ...
P61 (343 - 355), M. leprae
-
(Z)-Tonghaosu
The herbs of Glebionis coronaria.
-
Madecassoside
Madecassoside is a pentacyclic triterpene extracted from Centella asitica (L.) with anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-aging activities.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


