AR-9281
CAS No. 913548-29-5
AR-9281( APAU )
Catalog No. M22923 CAS No. 913548-29-5
AR9281 is a potent and selective inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (s-EH) potentially for the treatment of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 73 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 105 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 158 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 284 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 428 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 626 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAR-9281
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAR9281 is a potent and selective inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (s-EH) potentially for the treatment of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
-
DescriptionAR9281 is a potent and selective inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (s-EH) potentially for the treatment of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
-
In VitroAR-9281 (APAU) has inhibitory activity for human sEH (HsEH) and murine sEH (MsEH) with IC50 values of 13.8 nM and 1.7 nM, respectively.
-
In VivoAR-9281 (APAU) (oral, 150-200 mg/dL, for 6 weeks) enhances the therapeutic effects of EETs, slows progression of hyperglycemia, protects the myocyte structure, and reduces Ca2+ dysregulation and SERCA remodeling in hyperglycemic rats. Animal Model:T2DM rat model Dosage:150-200 mg/dL Administration:oral(drinking), for 6 weeks Result:Attenuated the progressive increase of blood glucose concentration and preserved mitochondrial structure and myofibril morphology in cardiac myocytes.Protected the intracellular Ca2+ effector system. Had less downregulation of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) and lowed expression of hypertrophic markers.
-
SynonymsAPAU
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptors-EH
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number913548-29-5
-
Formula Weight319.44
-
Molecular FormulaC18H29N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:25 mg/mL (78.26 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
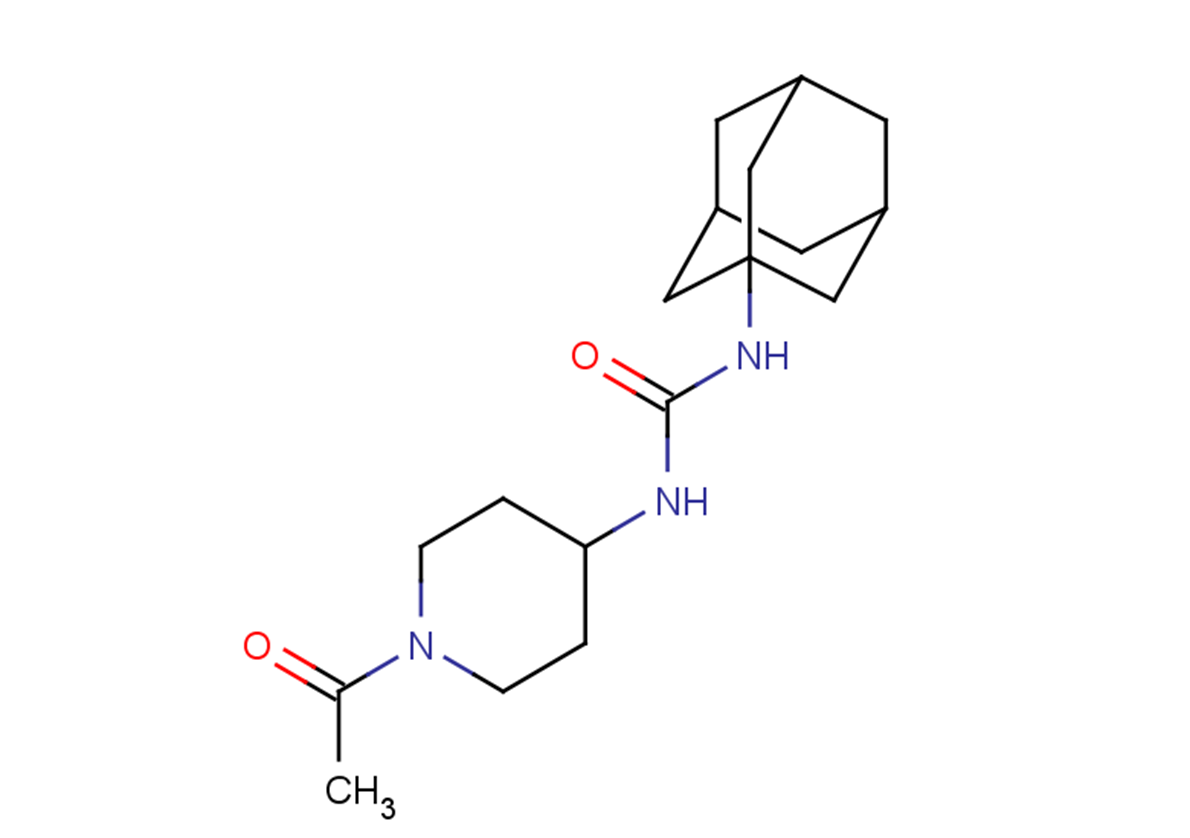
SMILESCC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)NC(=O)NC23CC4CC(CC(C4)C2)C3
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Chen D, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AR9281, an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase, in single- and multiple-dose studies in healthy human subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;52(3):319-28.
molnova catalog



related products
-
CMF019
CMF019 is a potent agonist of the Apelin receptor (APJ) with G protein bias. CMF019 binds to APJ (pKis: 8.58, 8.49, and 8.71 for the human, rat, and mouse).
-
7-Bromo-2,4-diaminoq...
7-Bromo-2, 4-diaminoquinazoline is an active biochemical.
-
Maculosidin
Maculosidine affect the PS I electron acceptors on leaf discs, it can inhibit ATP synthesis, basal, phosphorylating and uncoupled electron transport acting as Hill reaction inhibitors on spinach chloroplasts.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


