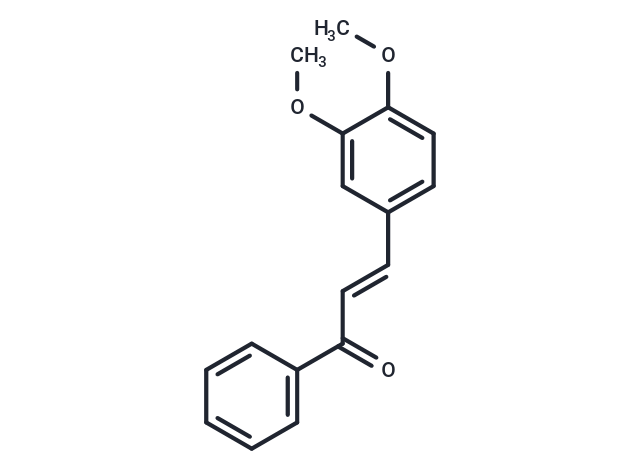
3,4-Dimethoxychalcone
CAS No. 5416-71-7
3,4-Dimethoxychalcone( —— )
Catalog No. M37752 CAS No. 5416-71-7
3,4-Dimethoxychalcone is a natural product found in the flowers of Arrabidaea brachypoda.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3,4-Dimethoxychalcone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3,4-Dimethoxychalcone is a natural product found in the flowers of Arrabidaea brachypoda.
-
Description3,4-Dimethoxychalcone is a Caloric restriction mimetics (CRMs). 3,4-Dimethoxychalcone induces the deacetylation of cytoplasmic proteins and stimulates autophagy flux. 3,4-Dimethoxychalcone can be used for cardiac and cancer diseases research.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5416-71-7
-
Formula Weight268.31
-
Molecular FormulaC17H16O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (372.70 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCOC1=CC=C(\C=C\C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C1OC
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Okolo EN, et al. New chalcone derivatives as potential antimicrobial and antioxidant agent. Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 5;11(1):21781.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
3β-Hydroxy-7β,25-dim...
3β-Hydroxy-7β,25-dimethoxycucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al
-
3-Hydroxy-6-methoxyf...
3-Hydroxy-6-methoxyflavone can be used in combination with antibiotics to treat ESKAPE pathogen infections.
-
4-[(2,4-dioxo-1,3-th...
4-[(2,4-dioxo-1,3-thiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl]benzoic acid is a chemical compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


