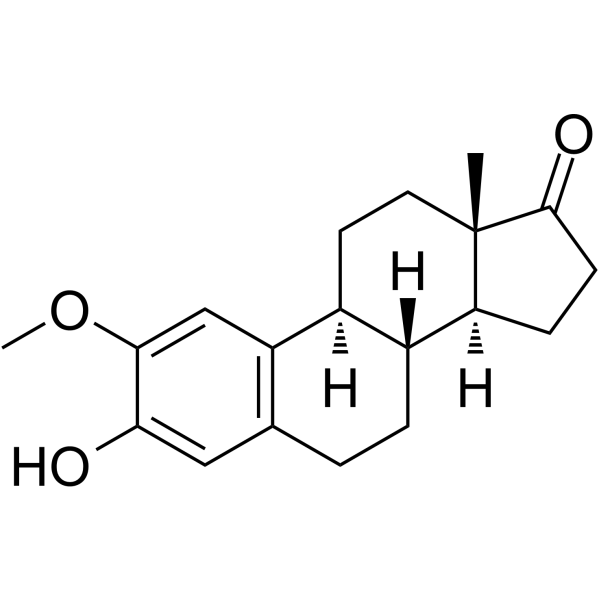
2-Methoxyestrone
CAS No. 362-08-3
2-Methoxyestrone( —— )
Catalog No. M26533 CAS No. 362-08-3
2-Methoxyestrone is a methoxylated catechol estrogen and the principal metabolite of 2-hydroxyestrone, a nonuterotropic metabolite of estradiol.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 110 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 160 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Methoxyestrone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Methoxyestrone is a methoxylated catechol estrogen and the principal metabolite of 2-hydroxyestrone, a nonuterotropic metabolite of estradiol.
-
Description2-Methoxyestrone is a methoxylated catechol estrogen and the principal metabolite of 2-hydroxyestrone, a nonuterotropic metabolite of estradiol.(In Vivo):2-Methoxyestrone, given at noon of proestrus, significantly augments the magnitude of the preovulatory prolactin rise possibly by inhibiting the formation of endogenous 2-hydroxyestrogens in the brain.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
Recptorprolyl endopeptidase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number362-08-3
-
Formula Weight300.398
-
Molecular FormulaC19H24O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (166.45 mM)
-
SMILES[H][C@@]12CCC(=O)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@]1([H])c3cc(OC)c(O)cc3CC[C@@]21[H]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kato A, Fukunari A, Sakai Y, Nakajima T. Prevention of amyloid-like deposition by a selective prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor, Y-29794, in senescence-accelerated mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Oct;283(1):328-35. PubMed PMID: 9336340.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(±) Anabasine
(±) Anabasine is a biphasic muscle relaxant.
-
delta-Valerobetaine
delta-Valerobetaine is a precursor of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO).
-
Acetamide
Acetamide is found in red beetrootis used primarily as a solvent and a plasticizer.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


