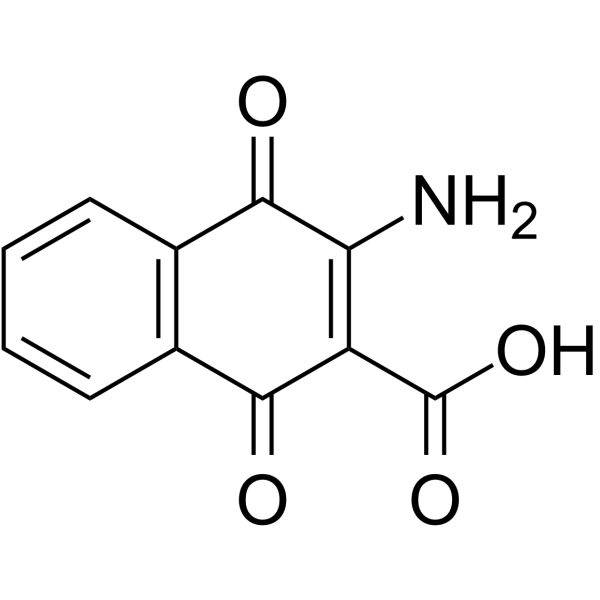
2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
CAS No. 173043-38-4
2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone( —— )
Catalog No. M31781 CAS No. 173043-38-4
2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is the electron transfer mediator, can change glucose metabolism of the homofermentative lactic acid bacteria.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 627 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is the electron transfer mediator, can change glucose metabolism of the homofermentative lactic acid bacteria.
-
Description2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is the electron transfer mediator, can change glucose metabolism of the homofermentative lactic acid bacteria. 2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is a novel growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, it affects the end-product profile of bifidobacteria through the mediated oxidation of NAD(P)H
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number173043-38-4
-
Formula Weight217.18
-
Molecular FormulaC11H7NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
L-Histidine monohydr...
Histidine (abbreviated as His or H) is an alpha-amino acid. The L-isomer is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids i.e. the building blocks of proteins.
-
12-Dihexadecanoyl-sn...
PE(14:0/14:0) is a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE or GPEtn). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylethanolamine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. PE(14:0/14:0) in particular consists of two chains of myristic acid at the C-1 and C-2 positions. The myristic acid moieties are derived from nutmeg and butter.
-
(R)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-di...
(R)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-diphenylheptan-3-one is extracted from the rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum, a Chinese medicinal herb. (R)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-diphenylheptan-3-one inhibits melanogenesis in theophylline-stimulated murine B16 melanoma 4A5 cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


