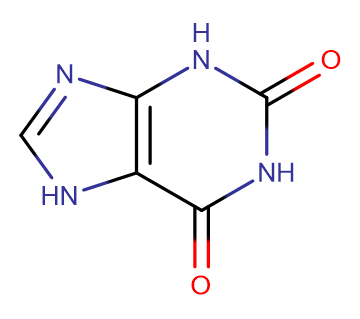
2,6-Dihydroxypurine
CAS No. 69-89-6
2,6-Dihydroxypurine( Xanthine )
Catalog No. M15681 CAS No. 69-89-6
A purine base found in most body tissues and fluids, certain plants, and some urinary calculi.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2,6-Dihydroxypurine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA purine base found in most body tissues and fluids, certain plants, and some urinary calculi.
-
DescriptionA purine base found in most body tissues and fluids, certain plants, and some urinary calculi. It is an intermediate in the degradation of adenosine monophosphate to uric acid, being formed by oxidation of hypoxanthine. The methylated xanthine compounds caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline and their derivatives are used in medicine for their bronchodilator effects.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsXanthine
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorPNP2| XPT
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number69-89-6
-
Formula Weight152.11
-
Molecular FormulaC5H4N4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 69 mg/L (at 16 °C)
-
SMILESO=C(N1)NC2=C(NC=N2)C1=O
-
Chemical Name1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Overington JP, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(Iso)-Atagabalin HCl
(Iso)-Atagabalin HCl(isomer-Atagabalin HCl) is an alpha -2- delta ligand that can be used to treat non-restorative sleep.
-
METHYL UNDECANOATE
Methyl undecanoate is an internal standard in gas-liquid chromatogram.
-
Licoisoflavanone
Licoisoflavanone is a natural product from Licorice.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


