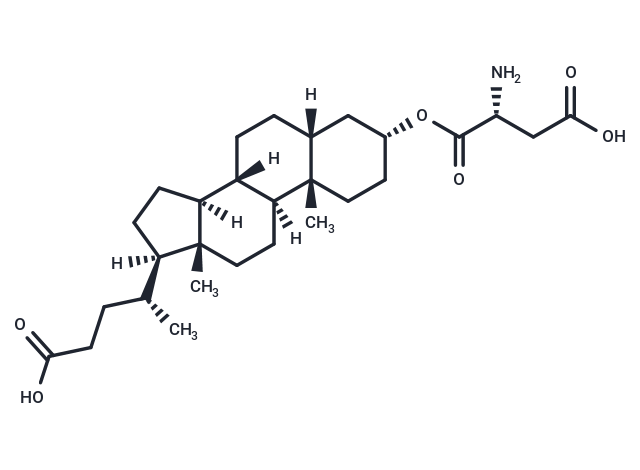
α-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1
CAS No. 881179-06-2
α-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M33184 CAS No. 881179-06-2
α-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1 is a noncompetitive inhibitor of α-2,3-sialyltransferase [IC50: 6 μM].
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1822 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2250 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Nameα-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Descriptionα-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1 is a noncompetitive inhibitor of α-2,3-sialyltransferase [IC50: 6 μM].
-
Descriptionα-2,3-sialyltransferase-IN-1 (Lith-O-Asp analog) is a noncompetitive α-2,3-sialyltransferase inhibitor with an IC50 of 6 μM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number881179-06-2
-
Formula Weight491.66
-
Molecular FormulaC28H45NO6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 103.7 mg/mL (210.92 mM)
-
SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])C[C@@H](CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CC(O)=O)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Chang KH, et al. Lithocholic acid analogues, new and potent alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase inhibitors. Chem Commun (Camb). 2006 Feb 14;(6):629-31.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
[Tyr36]-pTH-Related ...
[Tyr36]-pTH-Related Protein (1-36) (human, rat)
-
Biclotymol
Biclotymol is used in the study about infectious oropharyngeal diseases.
-
Dihydronitidine
Dihydronitidine is an alkaloid can be extracted from Zanthoxylum rhoifolium.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


