yibeissine
CAS No. 143502-51-6
yibeissine( —— )
Catalog No. M23599 CAS No. 143502-51-6
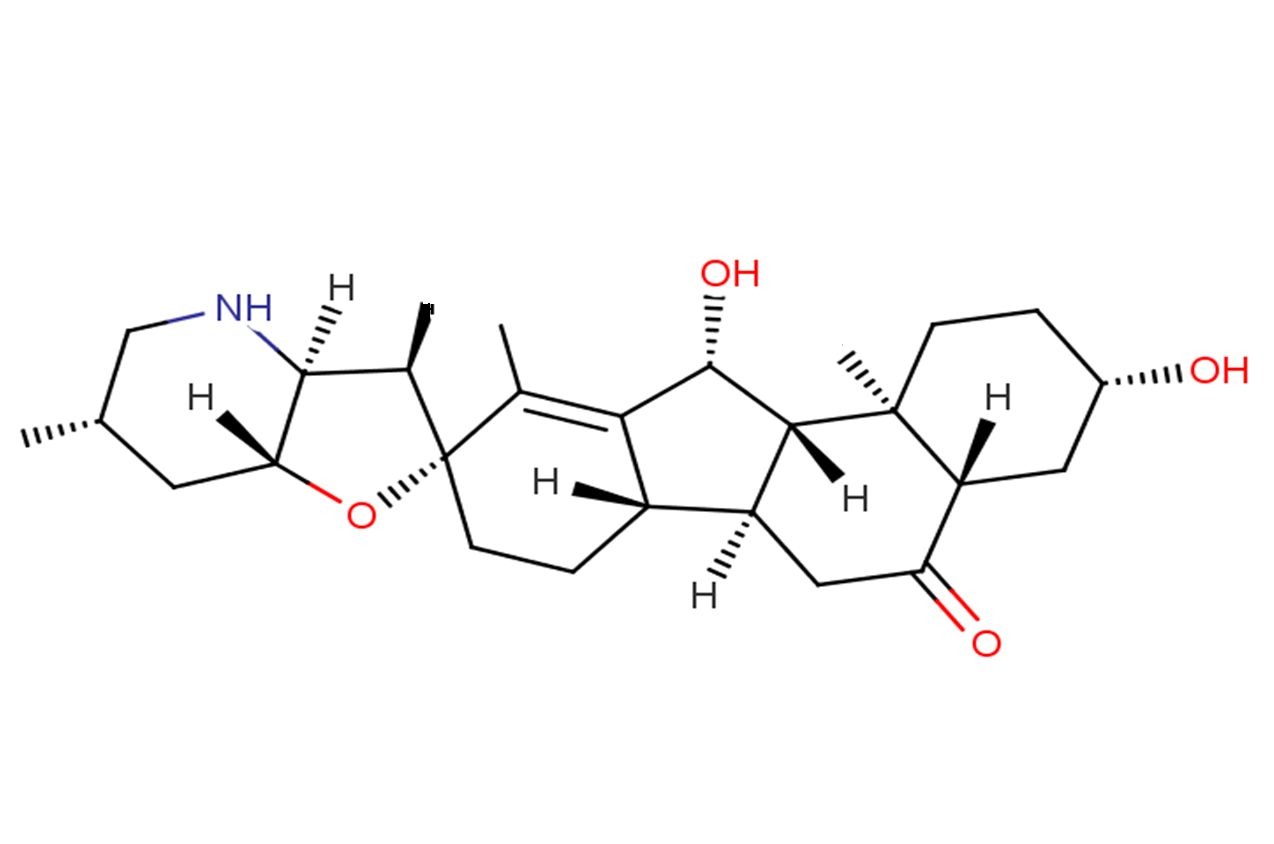
Yibeissine is a steroidal alkaloid isolated from the bulb of Fritillaria pallioiflora Schren.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 126 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 210 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 371 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Nameyibeissine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionYibeissine is a steroidal alkaloid isolated from the bulb of Fritillaria pallioiflora Schren.
-
DescriptionYibeissine is a steroidal alkaloid isolated from the bulb of Fritillaria pallioiflora Schren
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number143502-51-6
-
Formula Weight443.6
-
Molecular FormulaC27H41NO4?
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESCC1=C([C@@H]2O)[C@@]([C@@](CC3=O)([H])[C@@]2([H])[C@]([C@]3([H])C[C@H]4O)(CC4)C)([H])CC[C@@]1(O[C@@](C5)([H])[C@@]6([H])NC[C@H]5C)[C@@H]6C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Y J Xu, et al. Isolation and identification of yibeissine. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1992;27(2):121-4.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methoxyamine HCl
Methoxyamine HCl covalently binds to apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) DNA damage sites and inhibits base excision repair (BER), which may result in an increase in DNA strand breaks and apoptosis.
-
Codrituzumab
Codrituzumab (GC3) is a humanized antibody against the glypican-3 hepatocellular carcinoma protein that can be used in combination with sorafenib to study incurable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
-
His-Pro
His-Pro is a dipeptide consisting of histidyl and proline.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


