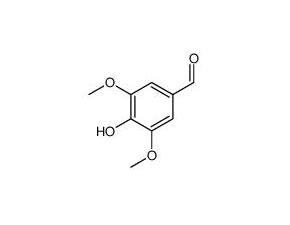
syringaldehyde
CAS No. 134-96-3
syringaldehyde( —— )
Catalog No. M17967 CAS No. 134-96-3
Syringaldehyde occurs in trace amounts widely in nature. Some species of insects use syringaldehyde in their chemical communication systems.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namesyringaldehyde
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSyringaldehyde occurs in trace amounts widely in nature. Some species of insects use syringaldehyde in their chemical communication systems.
-
DescriptionSyringaldehyde occurs in trace amounts widely in nature. Some species of insects use syringaldehyde in their chemical communication systems. Scolytus multistriatus uses it as a signal to find a host tree during oviposition.
-
In VitroSyringaldehyde inhibits COX-2 activity in a dosedependent manner with an IC50 of 3.5 μg/mL.
-
In VivoSyringaldehyde exerts anti-hyperglycemic effect in rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin. Apart from antioxidant capability, Syringaldehyde also has anti-inflammatory activity as it is found to have inhibitory action on cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX-2) in mouse macrophage cell line.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number134-96-3
-
Formula Weight182.17
-
Molecular FormulaC9H10O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (548.94 mM)
-
SMILESCOc1cc(cc(c1O)OC)C=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Meyer H.J. and Norris D.M., Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 17 July 1967, Volume 60, Number 4, pages 858-859.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dicyclohexyl ketone
Dicyclohexyl ketone is a vulcanization accelerator.
-
Gastrin Releasing Pe...
Gastrin Releasing Peptide (1-16), human
-
Cornoside
Cornoside and Iridoids are chemosystematic markers.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


