kaempferide
CAS No. 491-54-3
kaempferide( Kaempferide )
Catalog No. M18646 CAS No. 491-54-3
Kaempferide triglycoside inhibits the proliferation of native and estrogen receptor beta overexpressing colon cancer cells through a mechanism not mediated by ligand binding dependent estrogen receptor activation.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 261 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namekaempferide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKaempferide triglycoside inhibits the proliferation of native and estrogen receptor beta overexpressing colon cancer cells through a mechanism not mediated by ligand binding dependent estrogen receptor activation.
-
DescriptionKaempferide triglycoside inhibits the proliferation of native and estrogen receptor beta overexpressing colon cancer cells through a mechanism not mediated by ligand binding dependent estrogen receptor activation.
-
In VitroWestern Blot Analysis Cell Line:HepG2Concentration:5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM . Before treatment with OA (HY-N1446) (0.5 mM; 48 h)Incubation Time:48 h Result:Lowered the expression of proteins related to fat production, including sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD-1).Reduced the expression of two adipogenic transcription factors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and CCAAT enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ).Enhanced the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2).
-
In VivoAnimal Model:High-fat diet male C57BL/6J mice modelDosage:10 mg/kg Administration:Supplemented in daily diet, once daily for16 weeksResult:Reduced the weight, organ weight, and index of mice.Lowered the levels of glycolipids in mouse serum.Decreased the expression levels of inflammatory-related genes, including NF-κB, IL-6, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and TNF-α.Animal Model:Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) SD rat model.Dosage:0.1 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg Administration:Injection, Single dose. Before the I/R injury induced by Coronary Artery Ligation (CAL) in SD rats.Result:Significantly improved heart function, reduced myocardial injury by reducing myocardial enzyme levels, and dose-dependently reduced the area of myocardial infarction in rats.Significantly decreased serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), MDA, and ROS, while increasing serum levels of SOD.Downregulated the expression levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and cleaved caspase-3, and upregulated the phosphorylation expression levels of phospho-Akt (p-Akt) and phospho-glycogen synthase kinase-3β (p-GSK-3β).
-
SynonymsKaempferide
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorER
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number491-54-3
-
Formula Weight300.27
-
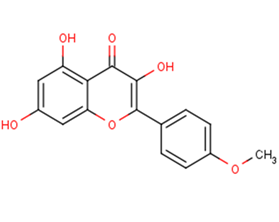
Molecular FormulaC16H12O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 20 mg/mL 66.61 mM;
-
SMILESCOc1ccc(cc1)c1c(c(=O)c2c(cc(cc2o1)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Song P,et al. [Comparison of effects of kaempferide and anhydroicaritin on biomineralization of cultured osteoblasts]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Jul;47(7):890-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tyrosine Kinase Pept...
Tyrosine Kinase Peptide 3 [RRLIEDAE-pY-AARG], Acetylated, Amide, Phosphorylated
-
(Rac)-SHIN2
(Rac)-SHIN2, a serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) inhibitor, enhances NOTCH1-driven in vivo survival of primary T-ALL in mice and is useful for studying T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL).
-
GRGDSPK
GRGDSPK is an inhibitory peptide for RGD-mediated adhesion between integrin and extracellular matrix molecules.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


