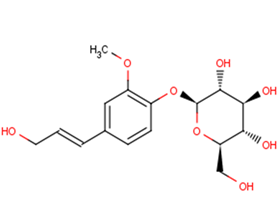
coniferin
CAS No. 531-29-3
coniferin( —— )
Catalog No. M18745 CAS No. 531-29-3
Coniferin has ATP-dependent transport activity and has anti-oxidation effects.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 222 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 383 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 617 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 872 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Nameconiferin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionConiferin has ATP-dependent transport activity and has anti-oxidation effects.
-
DescriptionConiferin has ATP-dependent transport activity and has anti-oxidation effects. Coniferin has preferred substrates for the coniferin beta-glucosidase, the chromogenic coniferin analogue show the exclusive presence of beta-glucosidase activity in the differentiating xylem, similar to peroxidase activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number531-29-3
-
Formula Weight342.34
-
Molecular FormulaC16H22O8
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (292.11 mM)
-
SMILESCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)/C=C/CO)O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
NAP
Davunetide is an eight amino acid snippet derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP), a neurotrophic factor that exists in the mammalian CNS. Davunetide possesses neuroprotective, neurotrophic and cognitive protective roperties. Davunetide, a microtubule-stabilizing peptide, interacts with and stabilises neuron-specific βIII-tubulin in vitro. Davunetide penetrates the blood-brain barrier and is non-toxic.Davunetide inhibits Aβ aggregation and Aβ-induced neurotoxicity.
-
Ophiopogonin B
Ophiopogonin B has antitumor activity and is a prospective inhibitor of PI3K/Akt.
-
EZH2-IN-13
EZH2-IN-13, a potent EZH2 inhibitor, exhibits potential anticancer activity and may be utilized to study diseases associated with EZH2 activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


