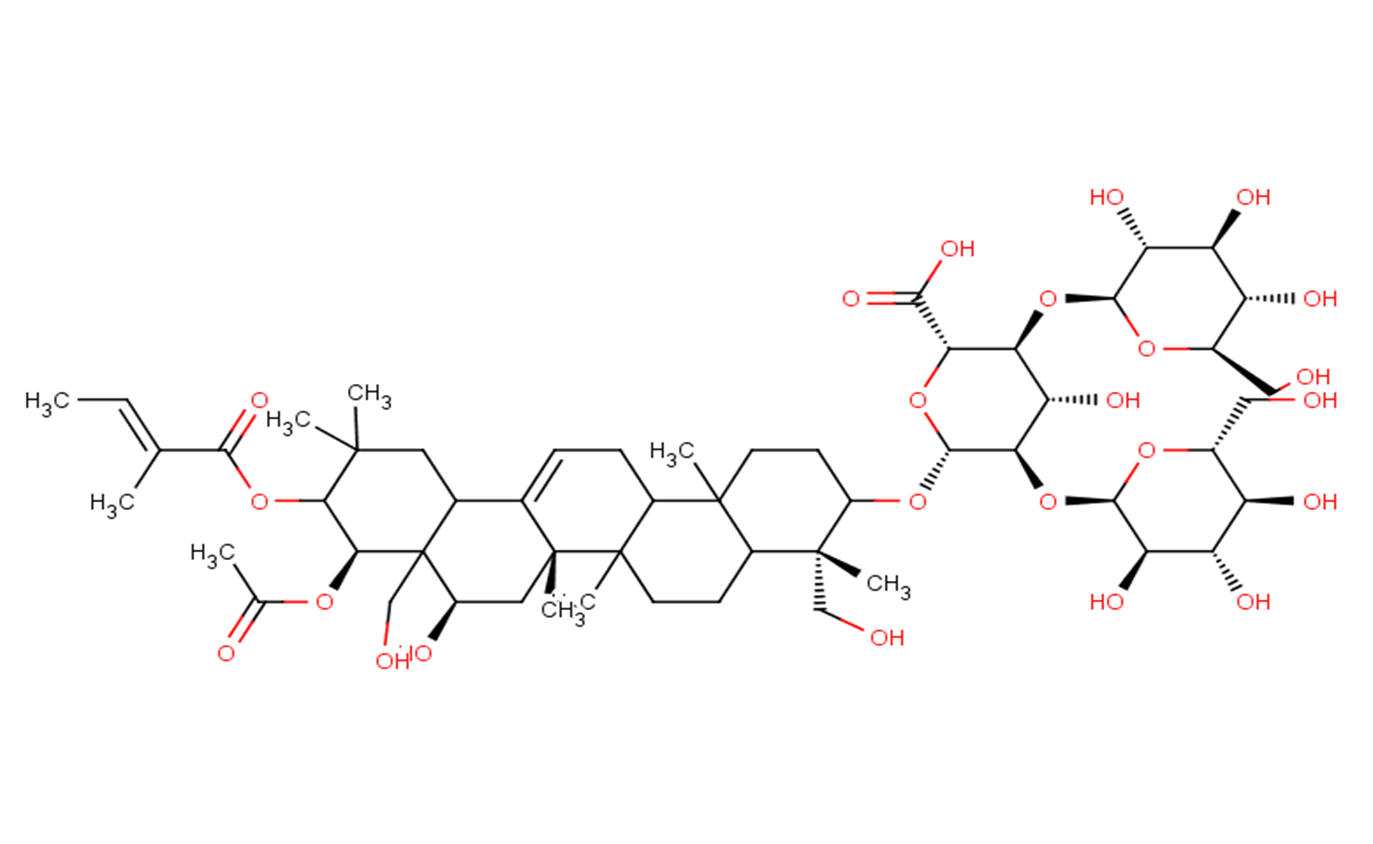
beta-Escin
CAS No. 11072-93-8
beta-Escin( AESCINE | B-escin )
Catalog No. M23308 CAS No. 11072-93-8
beta-Escin is a natural mixture of triterpenoid saponins isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namebeta-Escin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Descriptionbeta-Escin is a natural mixture of triterpenoid saponins isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds.
-
Descriptionbeta-Escin is a natural mixture of triterpenoid saponins isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds, can be used as a vasoprotective anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and anti-nociceptive agent.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAESCINE | B-escin
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorImmunology & Inflammation related
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number11072-93-8
-
Formula Weight1131.3
-
Molecular FormulaC55H86O24
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:95mg/mL (84 mM)
-
SMILESC/C=C(\C)/C(=O)OC1[C@@H](C2([C@@H](C[C@@]3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CCC([C@]5(C)CO)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)C(=O)O)O[C@H]7[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O7)CO)O)O)O)O)O[C@@H]8[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O8)CO)O)O)O)C)C)C2CC1(C)C)C)O)CO)OC(=O)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sipos W, Reutterer B, Frank M, et al. Escin inhibits type I allergic dermatitis in a novel porcine model. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;161(1):44-52. doi:10.1159/000343289
molnova catalog



related products
-
Gadobutrol
Gadobutrol is a nonionic paramagnetic contrast agent developed for tissue contrast enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
-
Cyclo(L-Ala-L-Pro)
Cyclo(L-Ala-L-Pro) and cyclo(L-Val-L-Pro) inhibit aflatoxin production of Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus in liquid medium at concentrations of several hundred uM without affecting fungal growth.
-
LX-4211 intermediate
LX-4211 intermediate a chemical compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


