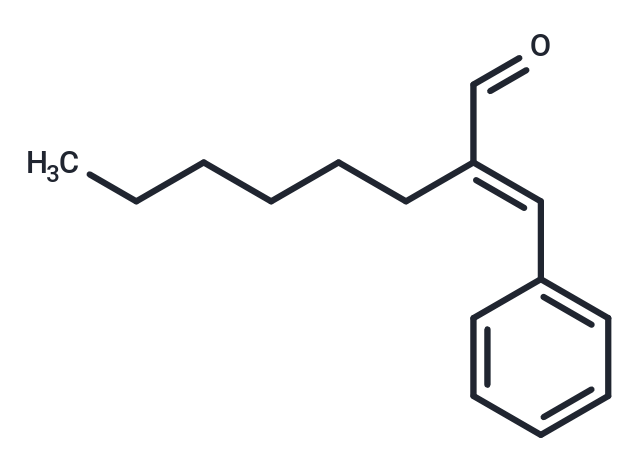
alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
CAS No. 101-86-0
alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde( —— )
Catalog No. M33095 CAS No. 101-86-0
alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde is a useful organic compound for research related to life sciences. The catalog number is T126521 and the CAS number is 101-86-0.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1G | 37 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namealpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Descriptionalpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde is a useful organic compound for research related to life sciences. The catalog number is T126521 and the CAS number is 101-86-0.
-
Descriptionα-Hexylcinnamaldehyde, a compound derived from Cinnamaldehyde. α-Hexylcinnamaldehyde has the potentialantimutagenic and chemosensitizing properties. α-Hexylcinnamaldehyde is widely used as an ingredient in many personal care, and as an additive in food and the pharmaceutical industry.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number101-86-0
-
Formula Weight216.32
-
Molecular FormulaC15H20O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (462.28 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCCCCCC\C(C=O)=C/C1=CC=CC=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Maria Grazia Sarpietro, et al. Interaction of α-Hexylcinnamaldehyde with a Biomembrane Model: A Possible MDR Reversal Mechanism. J Nat Prod. 2015 May 22;78(5):1154-9.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methyl 1,4-bisglucos...
Methyl 1,4-bisglucosyloxy-3-prenyl-2-naphthoate is a natural product.
-
2-Chloronaphthoquino...
2-Chloro-1, 4-naphthoquinone is a substituted naphthoquinone which is used as an insecticide and acaricide.
-
Acetylshikonin
Acetylshikonin can effectively inhibit tumor cells, it can be used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma cells expressing hepatitis B virus X protein (HBX) by inducing ER stress .



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


