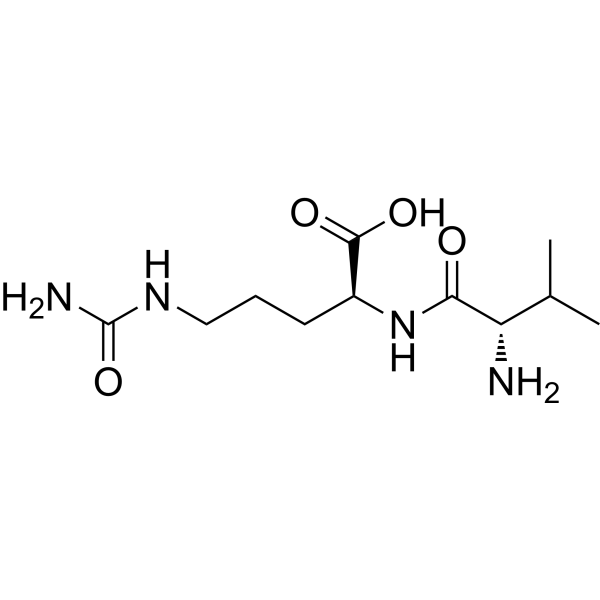
Val-Cit
CAS No. 159858-33-0
Val-Cit( —— )
Catalog No. M27024 CAS No. 159858-33-0
Val-Cit is a cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 215 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 312 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 530 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 758 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1044 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 2097 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVal-Cit
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVal-Cit is a cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
-
DescriptionVal-Cit is a cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).(In Vitro):ADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker.
-
In VitroADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAntibacterial| GRP78
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number159858-33-0
-
Formula Weight274.321
-
Molecular FormulaC11H22N4O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 62.5 mg/mL (227.84 mM)
-
SMILESCC(C)[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Machihara K, et al. Questiomycin A stimulates sorafenib-induced cell death via suppression of glucose-regulated protein 78. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Oct 7;492(1):33-40.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl...
The herbs of Gastrodia elata BL.
-
Tisotumab
Tisotumab (Anti-Human F3 Recombinant Antibody) is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting tissue factor (TF), utilized in antibody-conjugating drugs for cancer research.
-
α-Melanocyte Stimula...
α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone [Met5, Pro6, D-Phe7, D-Trp9, Phe10] (5-13) (MSHa)



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


