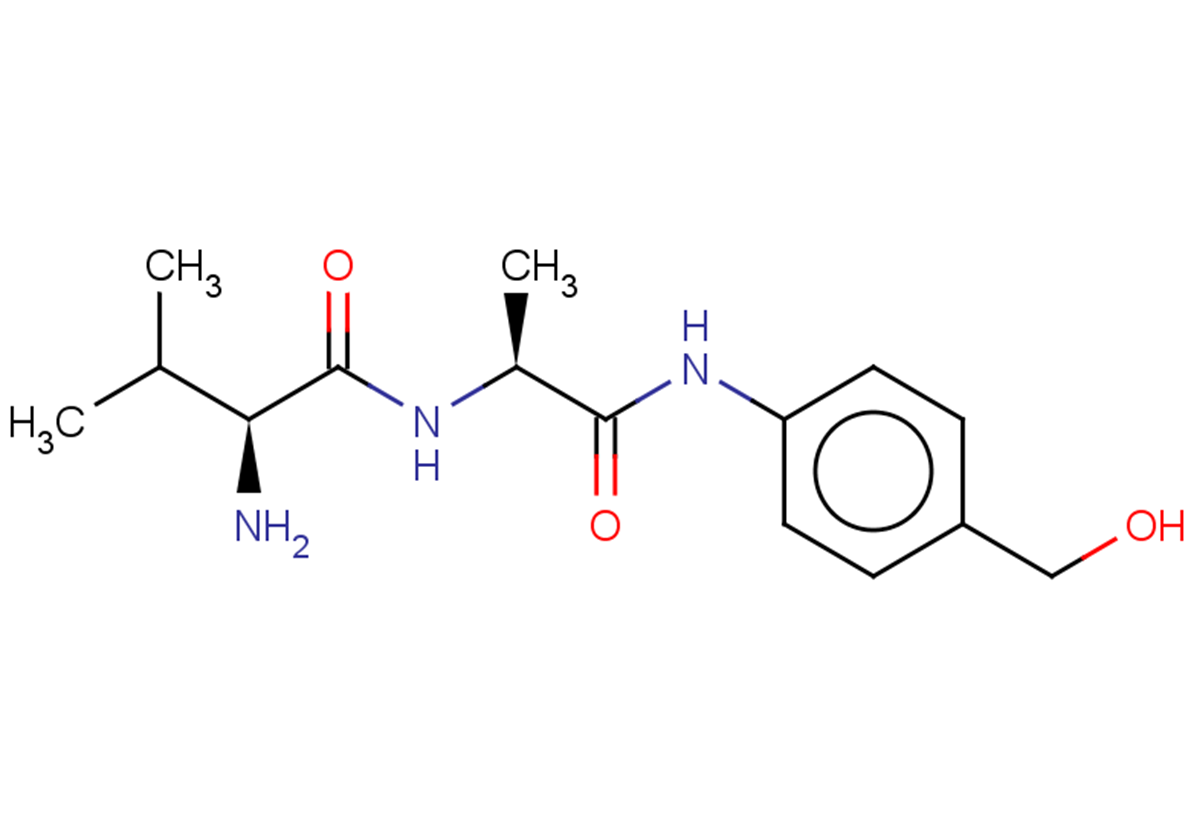
Val-Ala-PAB
CAS No. 1343476-44-7
Val-Ala-PAB( —— )
Catalog No. M23503 CAS No. 1343476-44-7
Val-Ala-PAB is a building block in the synthesis of Tesirine (a.k.a. SG3249), a clinical antibody-drug conjugate pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer payload.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 174 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 239 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 414 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 608 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 866 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1737 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVal-Ala-PAB
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVal-Ala-PAB is a building block in the synthesis of Tesirine (a.k.a. SG3249), a clinical antibody-drug conjugate pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer payload.
-
DescriptionVal-Ala-PAB is a building block in the synthesis of Tesirine (a.k.a. SG3249), a clinical antibody-drug conjugate pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer payload. Reagent in the preparation of pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimers and their antibody conjugates containing peptide linkers useful for treating proliferative including cancer.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1343476-44-7
-
Formula Weight293.36
-
Molecular FormulaC15H23N3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCC(C)[C@@H](C(N[C@@H](C)C(Nc1ccc(CO)cc1)=O)=O)N
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Angeloylgomisin Q
Angeloylgomisin Q is a natural product from Schizandra chinensis BAILL.
-
Epimagnolin A
Epimagnolin A is a lignan obtained from the flower buds of Magnolia fargesii, which is traditionally used in Asian medicine for treating headache and nasal congestion.?A herbal compound fargesin obtained from M. fargesii, has exerted anti-inflammatory effects in human monocytic THP-1 cells in the previous study.?it was demonstrated that epimagnolin A reduced phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)-induced IL-6 promoter activity and IL-6 production in human monocytic THP-1 cells.?
-
Tetrahydropalmatine ...
Tetrahydropalmatine (THP) is an alkaloid found in several different plant species, mainly in the Corydalis genus (Yan Hu Suo), but also in other plants such as Stephania rotunda.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


