Ubenimex
CAS No. 58970-76-6
Ubenimex( NK 421 | NSC 265489 | Ubenimex )
Catalog No. M15181 CAS No. 58970-76-6
Bestatin (Ubenimex) is a competitive aminopeptidase inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 59 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 101 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 159 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 264 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 655 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameUbenimex
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBestatin (Ubenimex) is a competitive aminopeptidase inhibitor.
-
DescriptionBestatin (Ubenimex) is a competitive aminopeptidase inhibitor, which is studied for use in the treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia.(In Vitro):Bestatin enhances ATRA-induced differentiation and inhibits ATRA-driven phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in ATRA-sensitive APL NB4 cells. Bestatin can not reverse the differentiation block in ATRA-resistant APL MR2 cells. CD13 ligation with anti-CD13 antibody WM-15 results in phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, reduces the inhibition of Bestatin on the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, and completely abolishes the enhancement of Bestatin on ATRA-inducing differentiation in NB4 cells. Bestatin (600 μM)-treated cells progress slower through the cell cycle due to decreased rate of cell growth and the frequency of cell division. Bestatin inhibits the frequency of mitosis and the inherent multinuclearity in D. discoideum, and is not cytotoxic to D. discoideum cells at 0-600 μM. Bestatin inhibits aminopeptidase activity in lysates of PsaA-GFP- and GFP-expressing cells by 69.39% and 39.93% of control, respectively. (In Vivo):Bestatin (20 μM) significantly reduces CD13 expression in diabetic mice and results a significant inhibition of MMP-9 specific gelationolytic band densities compared to diabetic vehicle-treated mice. Bestatin treatment significantly inhibits the expression of VEGF and heparanase in diabetic mice. Intravitreal bestatin treatment significantly downregulates the expression of both HIF-1α and VEGF in diabetic mice retinas. Furthermore, the upregulated expression of heparanase in diabetic mice retinas is significantly inhibited by intravitreal bestatin treatment. Bestatin (10, 1, and 0.1mg/kg, i.p.) treatment before the antigen-potentiated humoral response to SRBC results in an increased number of splenocytes producing hemolytic anti-SRBC antibodies (PFC) and the 2-ME-resistant serum hemagglutinin titer (at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg). Bestatin (1 and 0.1 mg/kg) administered to mice five times on alternate days after cyclophosphamide injection does not change the suppressive effect of the drug regarding the number of PFC, and even causes the further decrease of the total anti-SRBC hemagglutinins at dose of 1 mg/kg on day 7 after antigen stimulation.
-
In VitroBestatin enhances ATRA-induced differentiation and inhibits ATRA-driven phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in ATRA-sensitive APL NB4 cells. Bestatin can not reverse the differentiation block in ATRA-resistant APL MR2 cells. CD13 ligation with anti-CD13 antibody WM-15 results in phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, reduces the inhibition of Bestatin on the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, and completely abolishes the enhancement of Bestatin on ATRA-inducing differentiation in NB4 cells. Bestatin (600 μM)-treated cells progress slower through the cell cycle due to decreased rate of cell growth and the frequency of cell division. Bestatin inhibits the frequency of mitosis and the inherent multinuclearity in D. discoideum, and is not cytotoxic to D. discoideum cells at 0-600 μM. Bestatin inhibits aminopeptidase activity in lysates of PsaA-GFP- and GFP-expressing cells by 69.39% and 39.93% of control, respectively.
-
In VivoBestatin (20 μM) significantly reduces CD13 expression in diabetic mice and results a significant inhibition of MMP-9 specific gelationolytic band densities compared to diabetic vehicle-treated mice. Bestatin treatment significantly inhibits the expression of VEGF and heparanase in diabetic mice. Intravitreal bestatin treatment significantly downregulates the expression of both HIF-1α and VEGF in diabetic mice retinas. Furthermore, the upregulated expression of heparanase in diabetic mice retinas is significantly inhibited by intravitreal bestatin treatment. Bestatin (10, 1, and 0.1mg/kg, i.p.) treatment before the antigen-potentiated humoral response to SRBC results in an increased number of splenocytes producing hemolytic anti-SRBC antibodies (PFC) and the 2-ME-resistant serum hemagglutinin titer (at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg). Bestatin (1 and 0.1 mg/kg) administered to mice five times on alternate days after cyclophosphamide injection does not change the suppressive effect of the drug regarding the number of PFC, and even causes the further decrease of the total anti-SRBC hemagglutinins at dose of 1 mg/kg on day 7 after antigen stimulation.
-
SynonymsNK 421 | NSC 265489 | Ubenimex
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetLTR
-
RecptorLTA(4)H-h| APN
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number58970-76-6
-
Formula Weight308.37
-
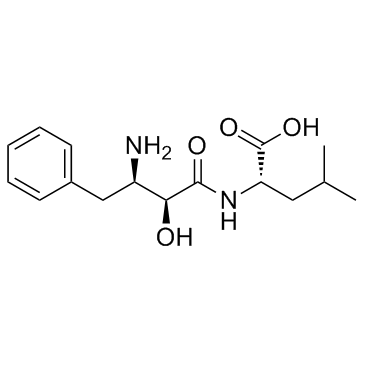
Molecular FormulaC16H24N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 0.4 mg/mL (1.29 mM)
-
SMILESCC(C)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)N)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sekine K, et al. Leukemia, 1999, 13(5), 729-734.
molnova catalog



related products
-
JNJ-7777120
JNJ-7777120 is the first potent and selective non-imidazole histamine H4 receptor antagonist with Ki of 4.5 nM, exhibits >1000-fold selectivity over the other histamin receptors.
-
Ontazolast
Ontazolast is a small molecule leukotriene B4 receptor (LTB4R) antagonist for the treatment of immune system disorders and respiratory diseases.Ontazolast is a candidate compound for the treatment of asthma.
-
γ-Linolenic Acid met...
γ-Linolenic Acid methyl ester is a weak leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptor antagonist.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


