UNC6934
CAS No. 2561494-77-5
UNC6934( —— )
Catalog No. M28780 CAS No. 2561494-77-5
UNC6934 is a chemical probe targeting the N-terminal PWWP (PWWP1) domain of NSD2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 205 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 331 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 560 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 797 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1071 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameUNC6934
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionUNC6934 is a chemical probe targeting the N-terminal PWWP (PWWP1) domain of NSD2.
-
DescriptionUNC6934 is a chemical probe targeting the N-terminal PWWP (PWWP1) domain of NSD2.(In Vitro):UNC6934 occupies the canonical H3K36me2-binding pocket of PWWP1, antagonizes PWWP1 interaction with nucleosomal H3K36me2 and selectively engages endogenous NSD2 in cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorATPase|Potassium Channel|Sodium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2561494-77-5
-
Formula Weight443.45
-
Molecular FormulaC24H21N5O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (56.38 mM)
-
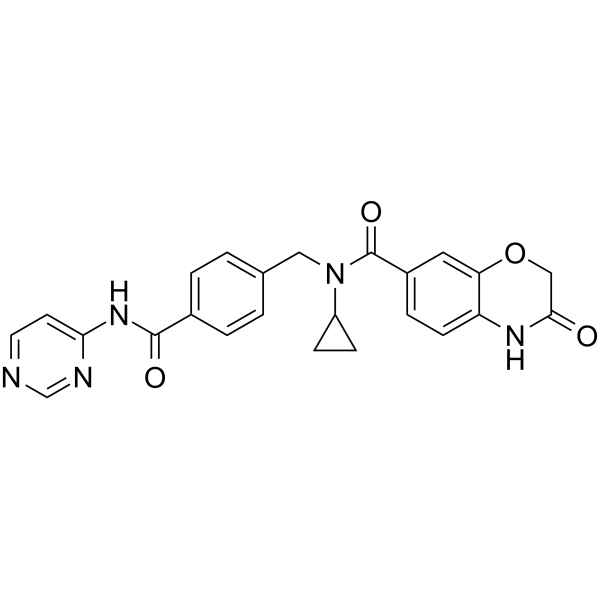
SMILESO=C(c1ccc(CN(C2CC2)C(c(cc2)cc(OC3)c2NC3=O)=O)cc1)Nc1ncncc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kohls S, et al. Method validation of a survey of thevetia cardiac glycosides in serum samples. Forensic Sci Int. 2012 Feb 10;215(1-3):146-51.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dioctanoylglycol
Dioctanoylglycol is a diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor.
-
Narirutin 4-glucosid...
The young fruits of Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck.
-
DSG Crosslinker
DSG Crosslinker is a cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


